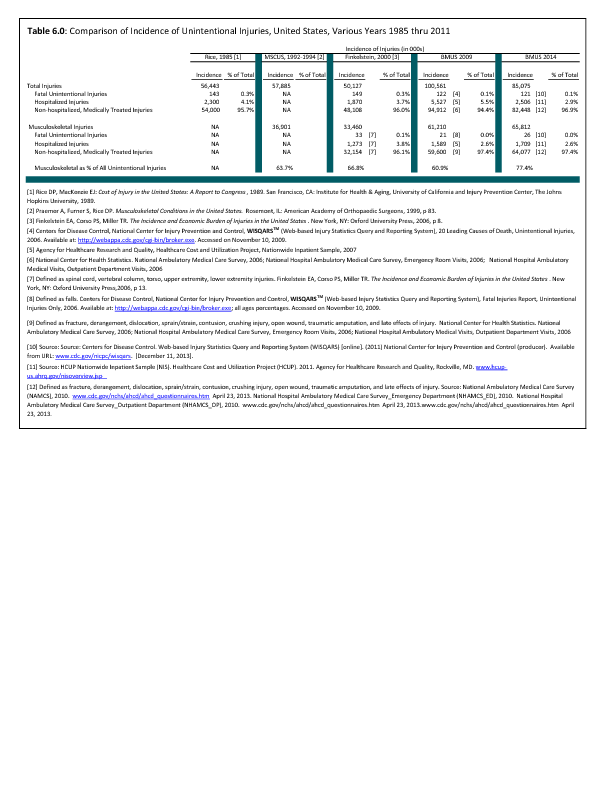
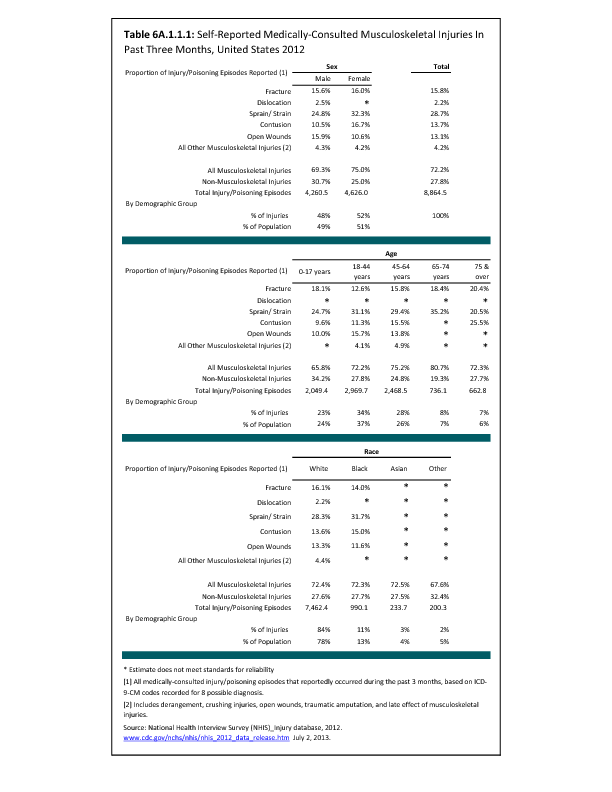
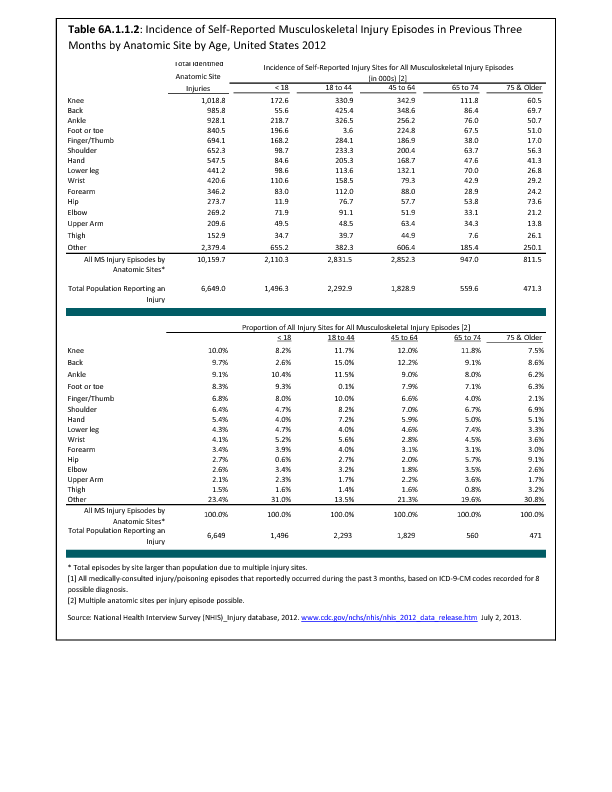
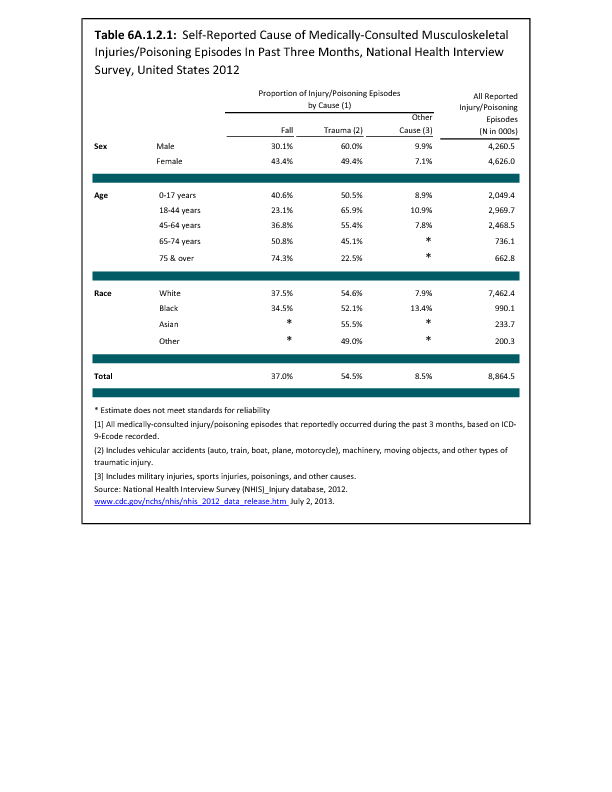
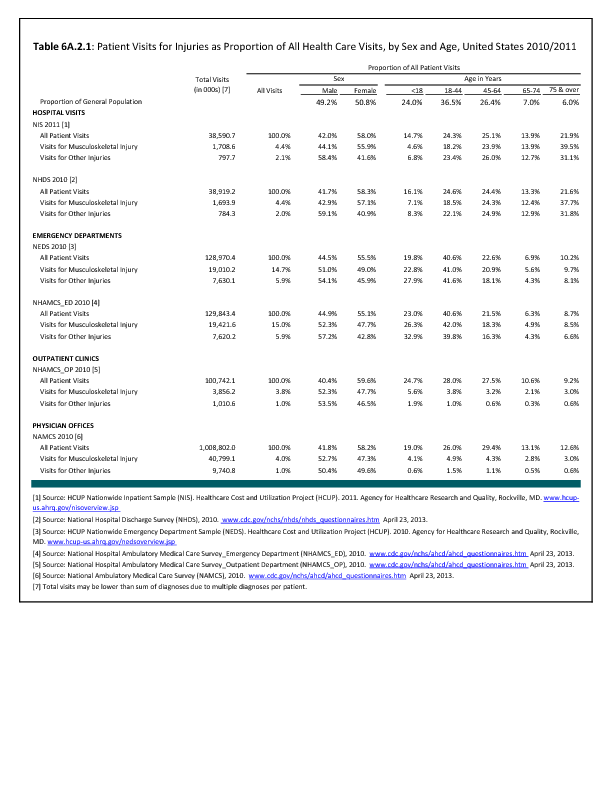
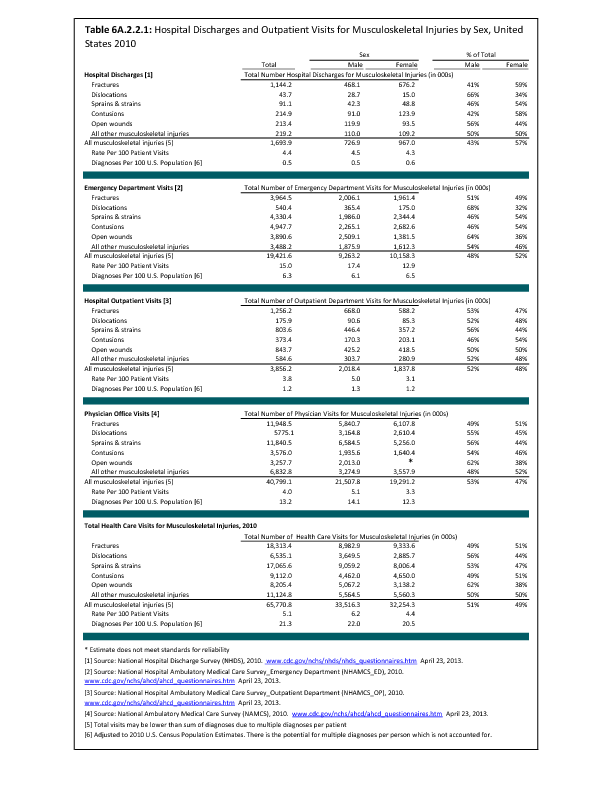
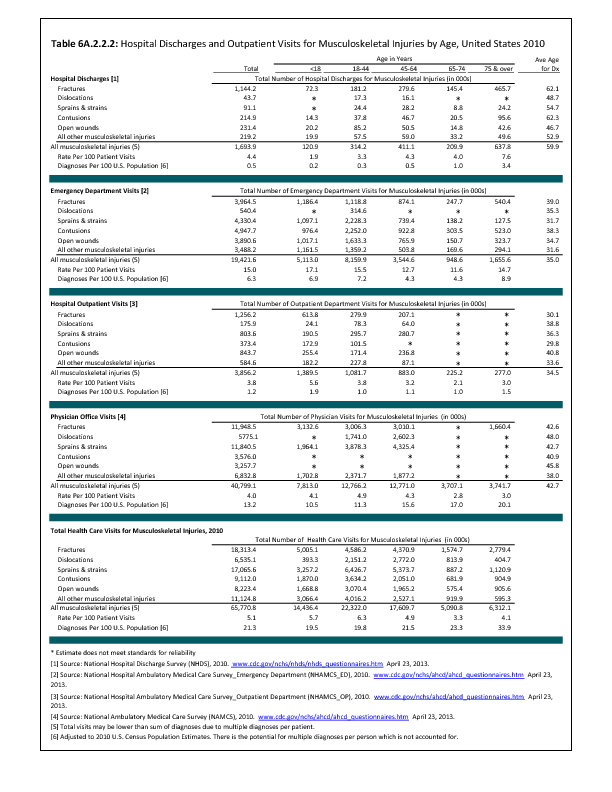
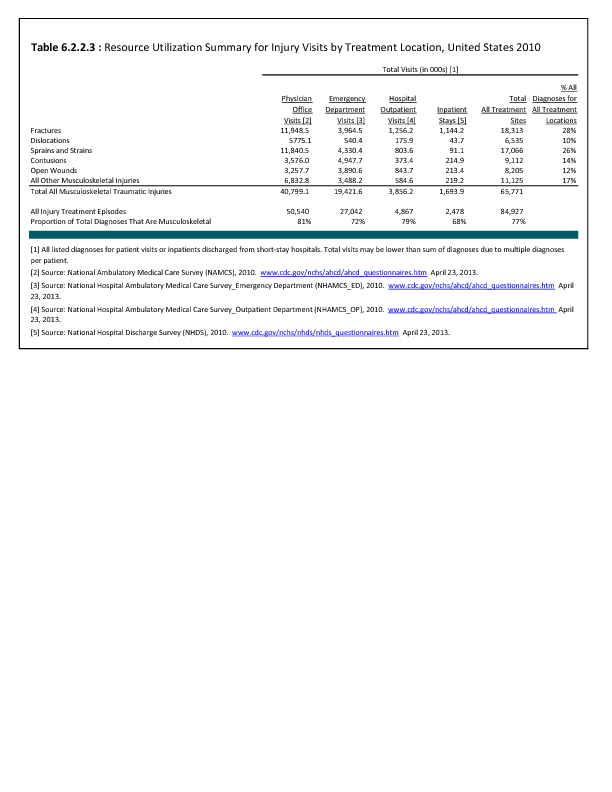
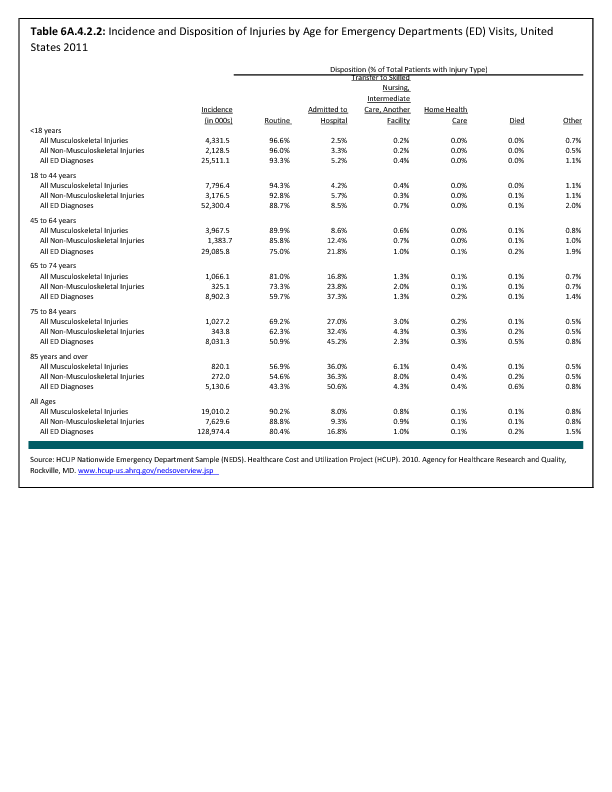
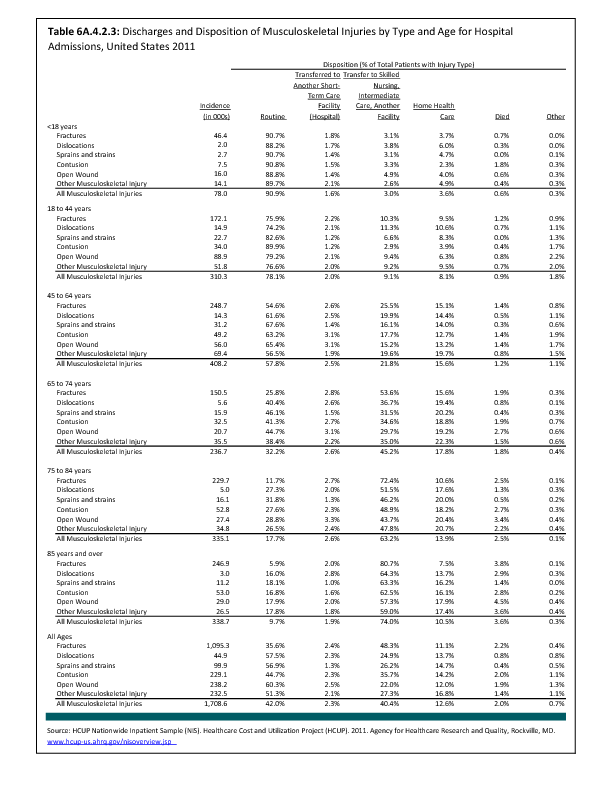
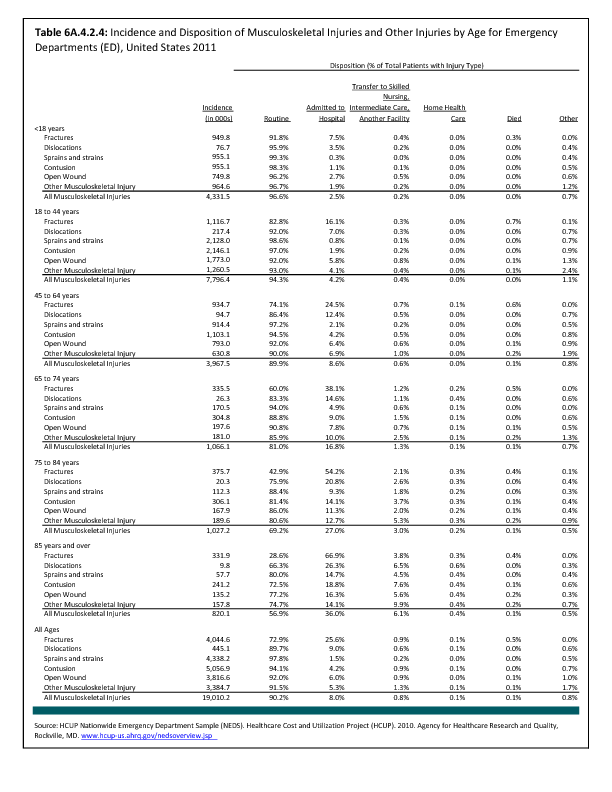
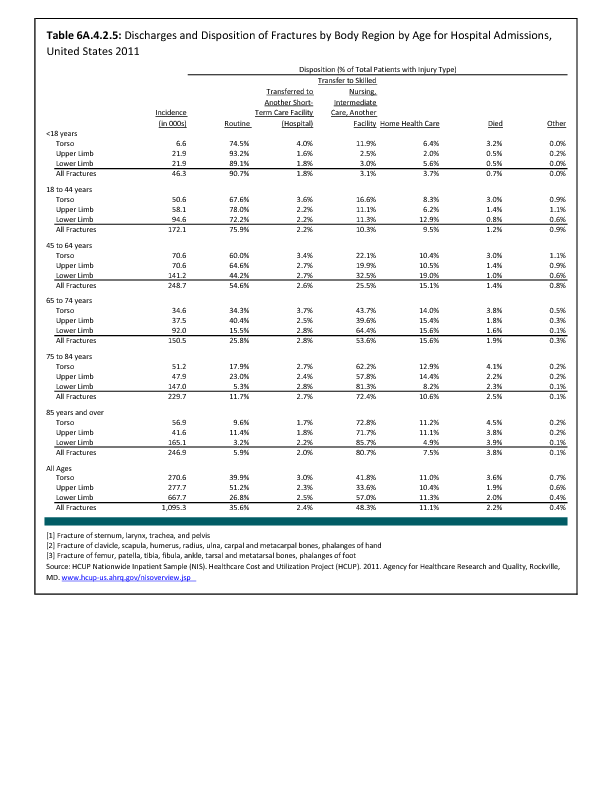
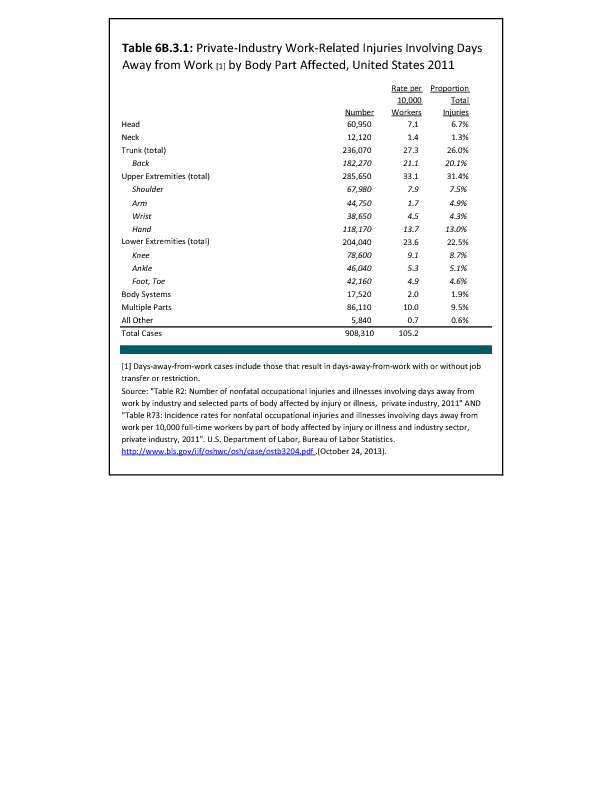
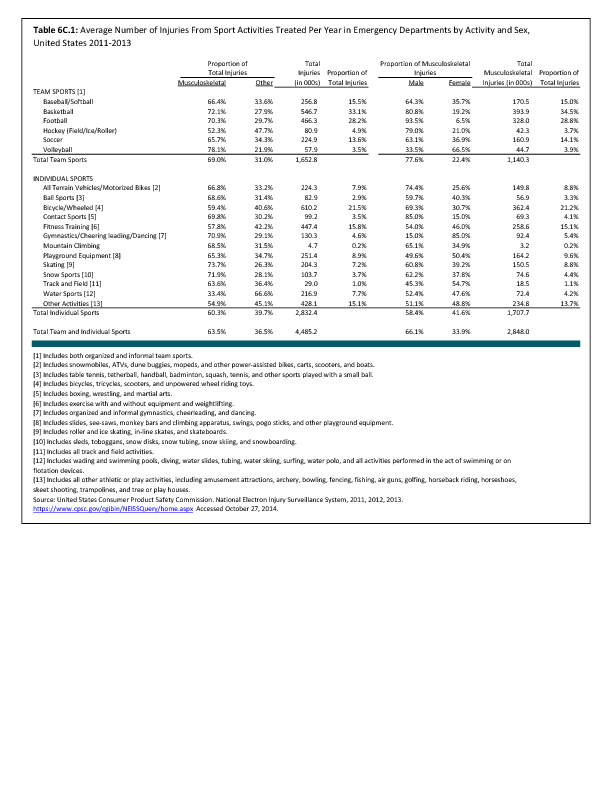
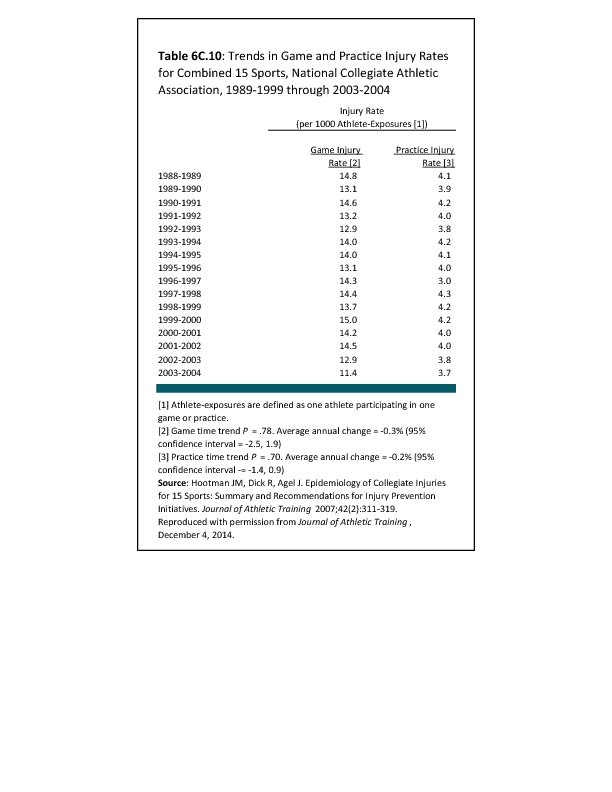
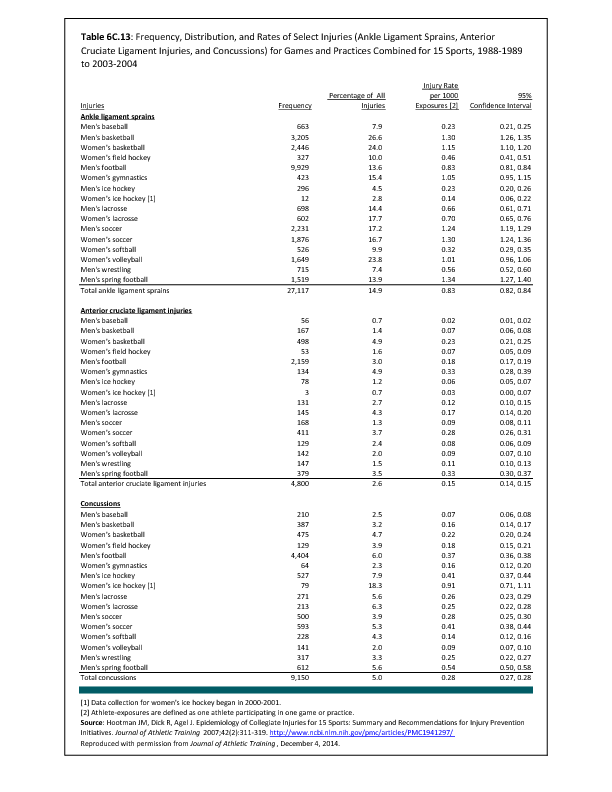
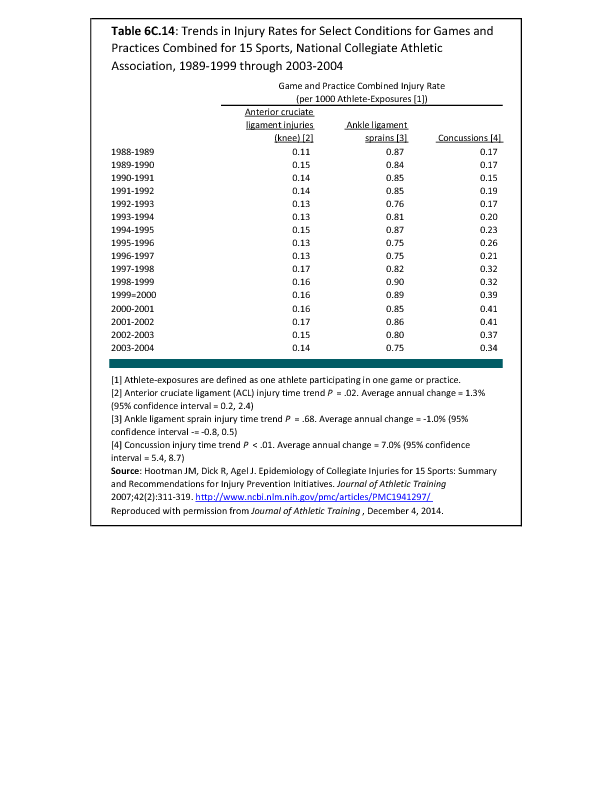
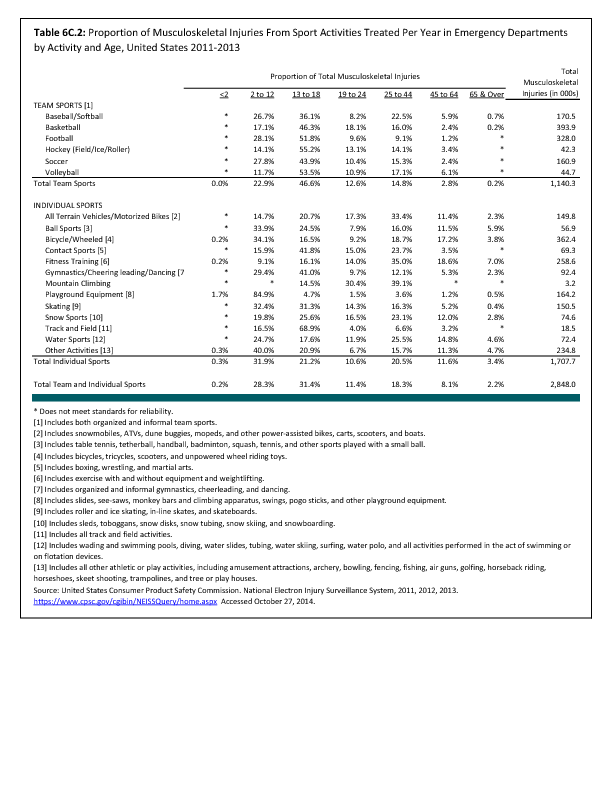
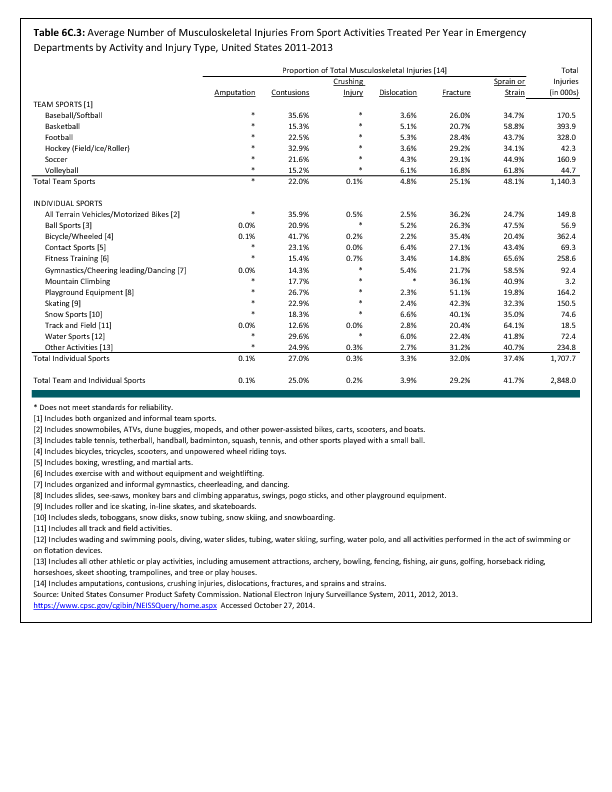
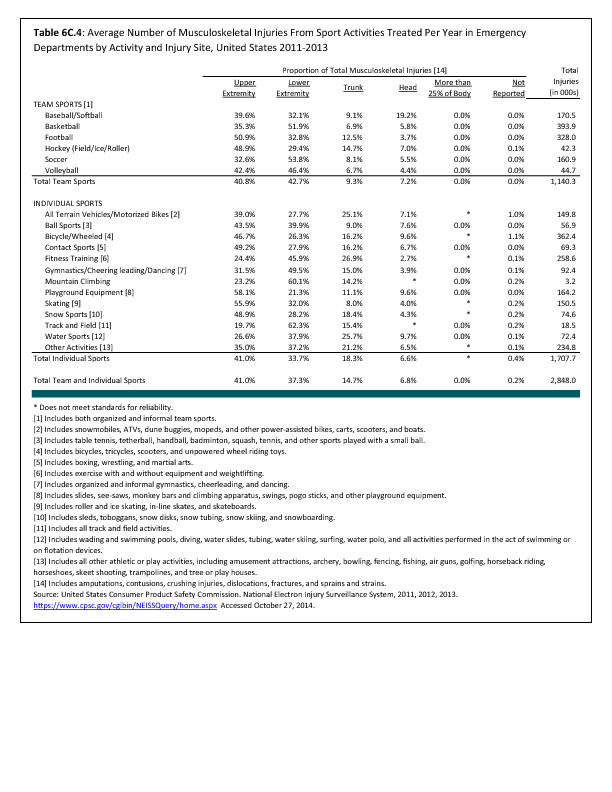
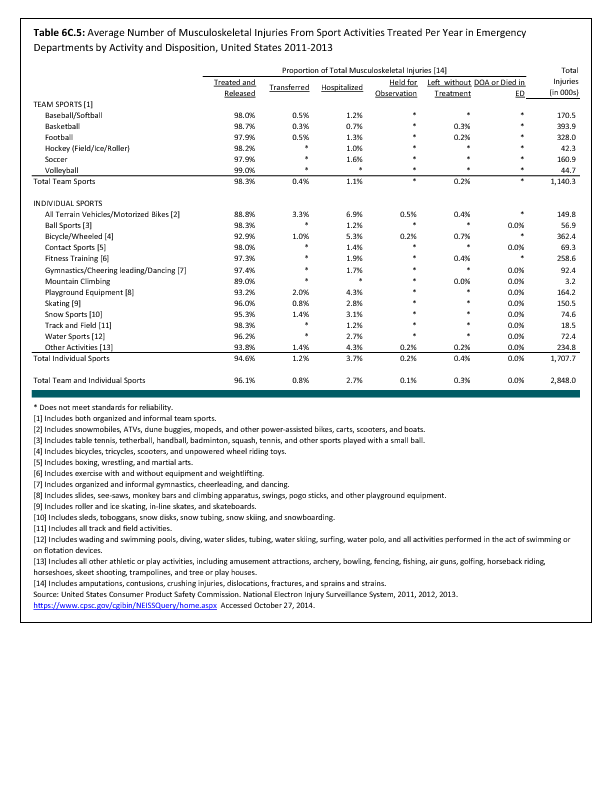
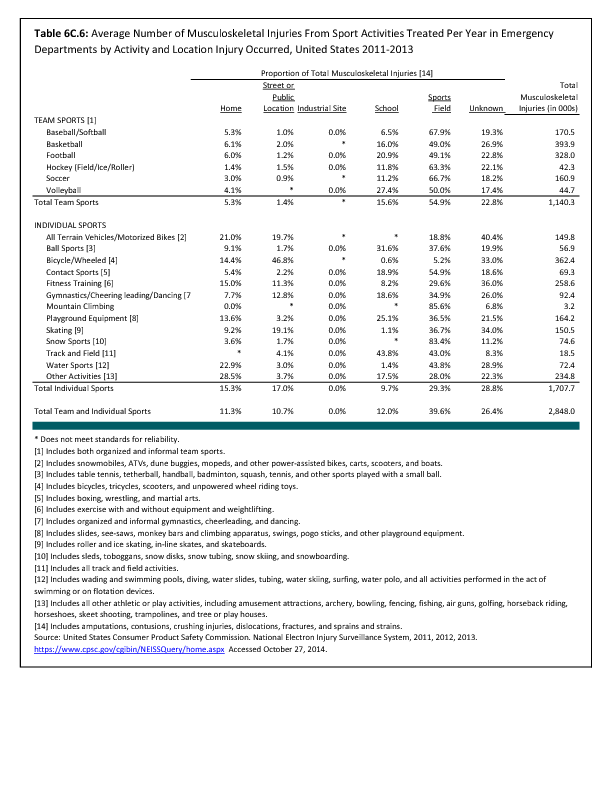
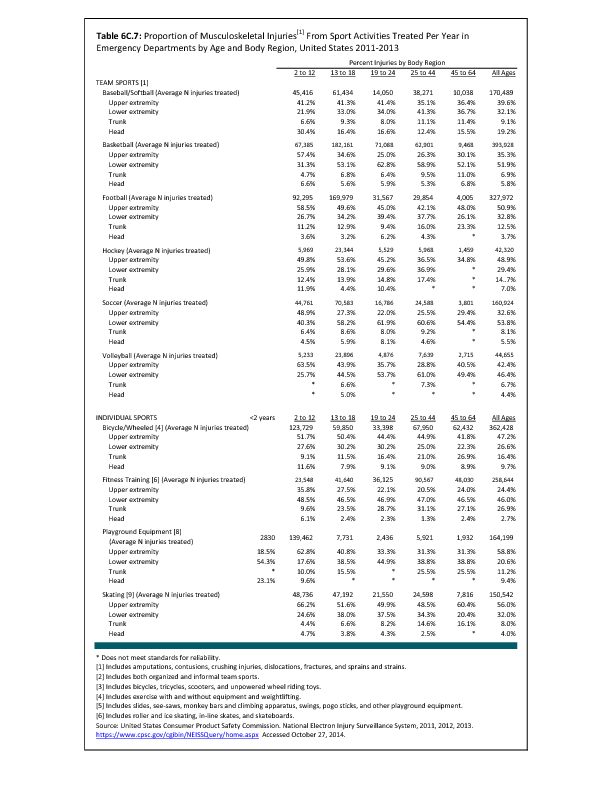
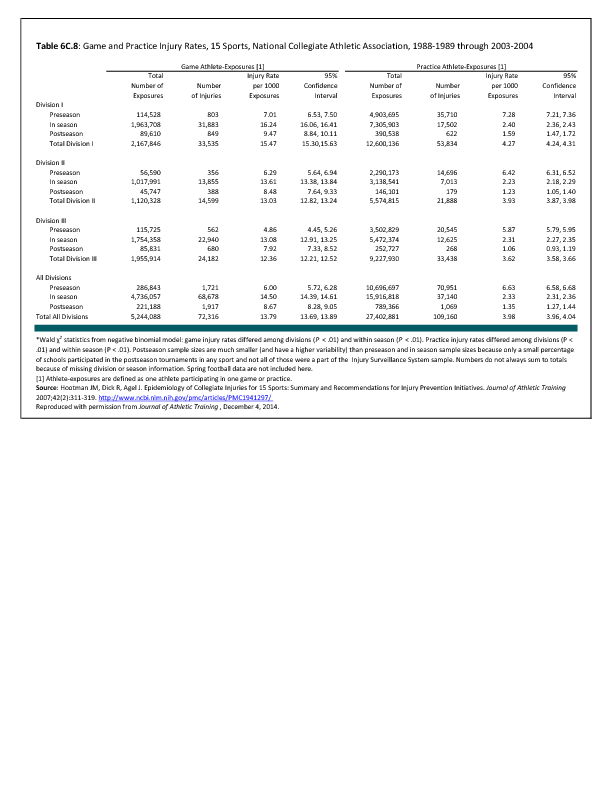
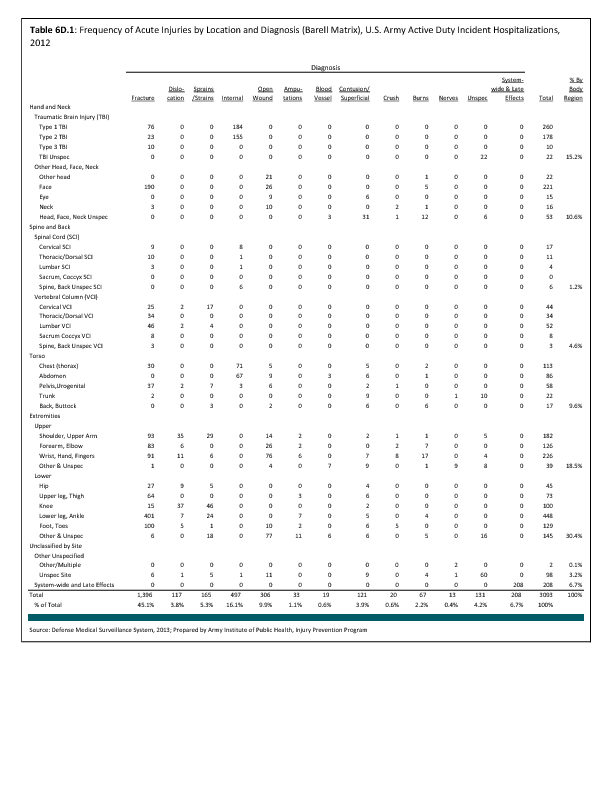
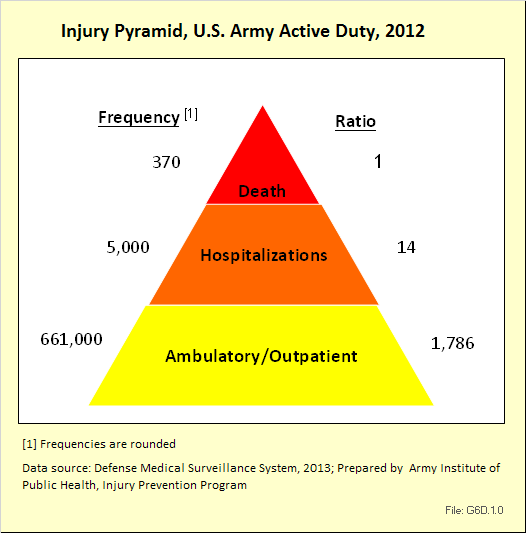
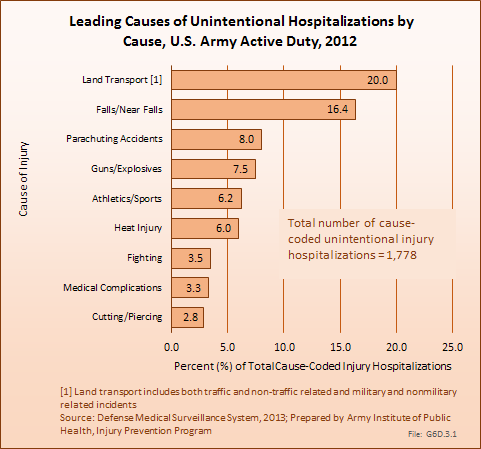
In 2012, there were 3,093 acute traumatic injuries (coded in the 800–900 ICD-9-CM code series) requiring hospitalization. Leading specific reasons for hospitalizations included fractures of the lower leg and/or ankle (13 %), facial fracture (6%), and fracture of the foot/toes (3%). Comparing all body regions, the lower extremity accounted for 30%, the upper extremity for 19%, and the head for 16%. Within the head region, traumatic brain injury, including skull fracture, accounted for 15%, and other specified head injuries accounted for less than 1%. (Reference Table 6D.1 PDF CSV)
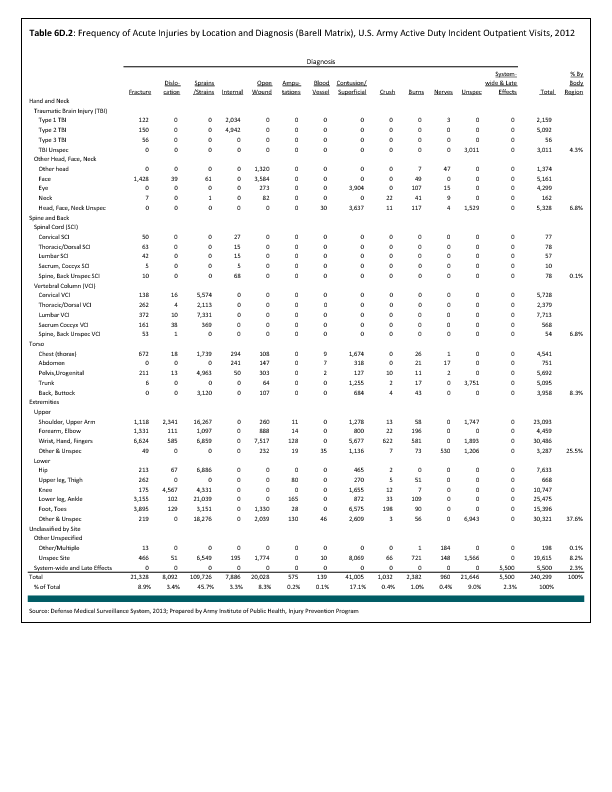
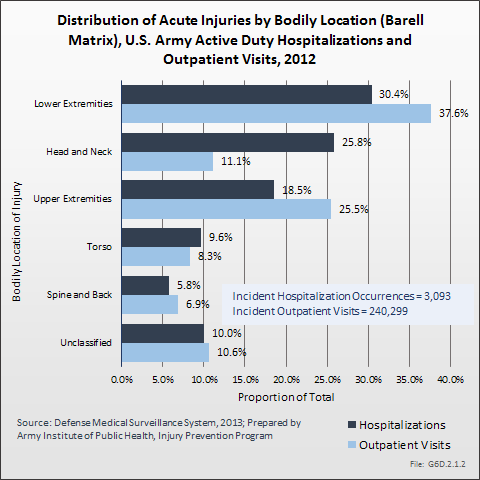
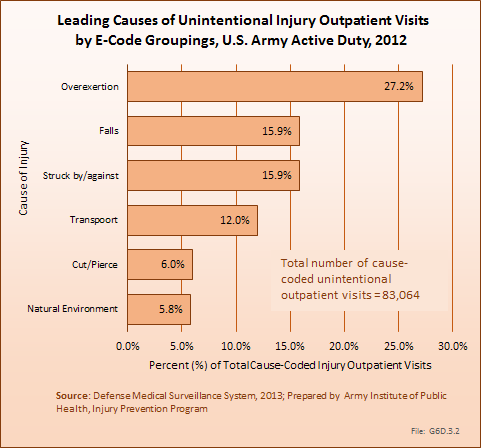
During the same year, US Army active duty, nondeployed soldiers incurred 240,299 acute traumatic injuries (coded in the 800–900 ICD-9-CM code series) for which outpatient care was required. Leading specific reasons for outpatient visits included strains/sprains to the lower leg and/or ankle (9%) and strains/sprains of the shoulder/upper arm (7%). Body regions most affected were lower extremities (38%), upper extremities (26%), and the head and neck region (TBI and other head, face, and neck) (11%). (Reference Table 6D.2 PDF CSV)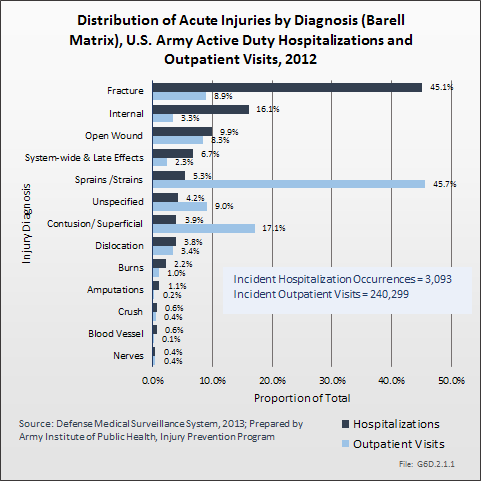
Edition:
- 2014

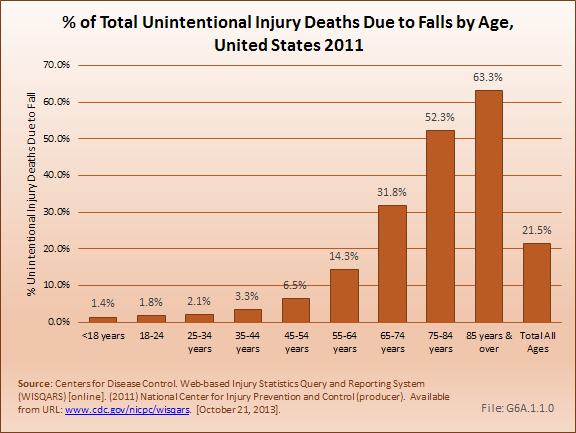
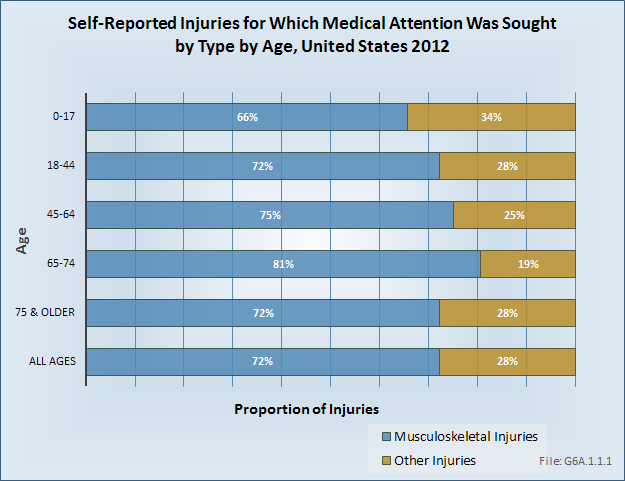
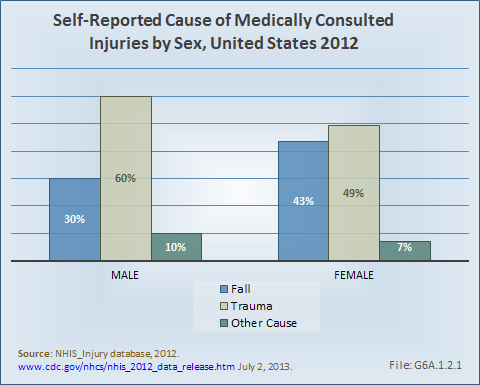
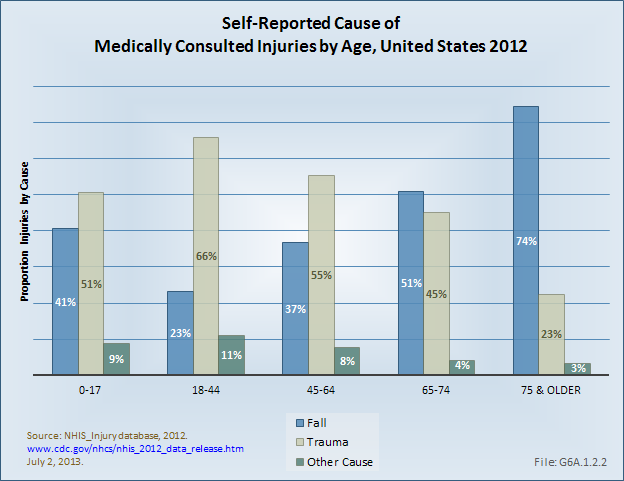
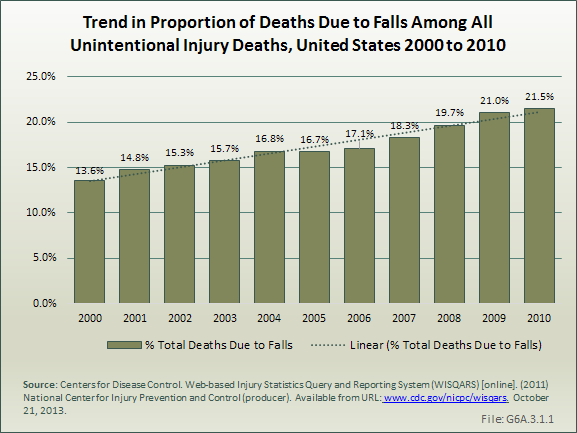
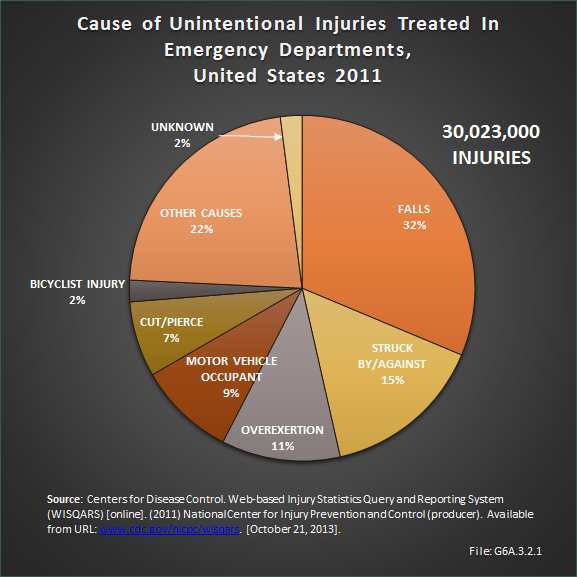
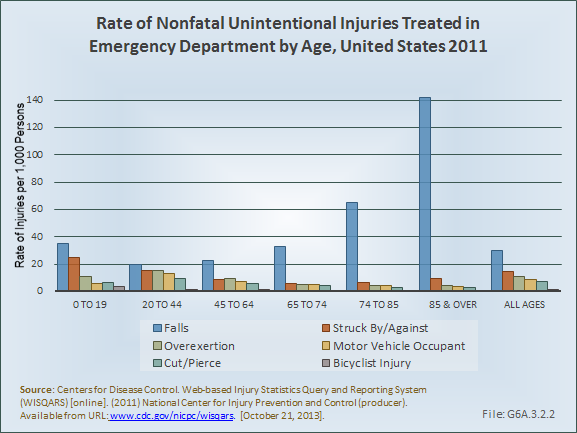
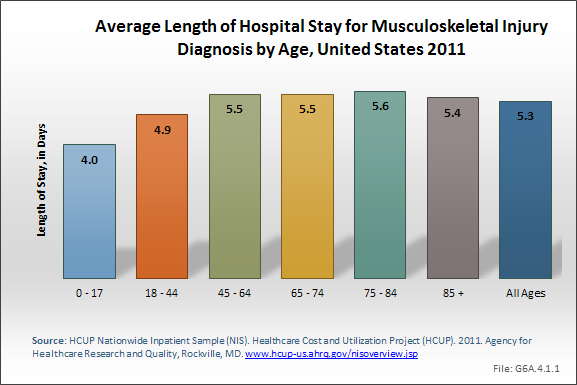
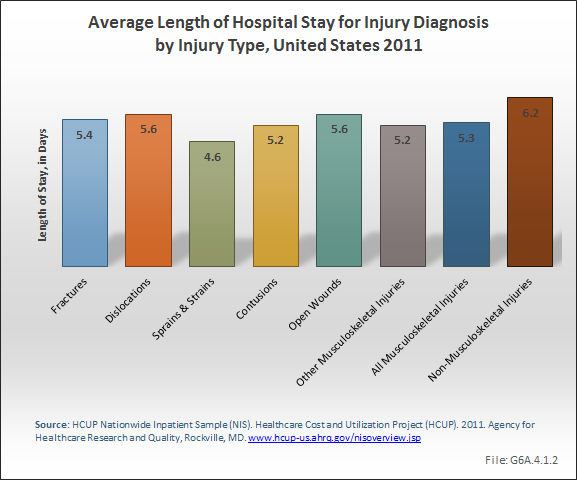
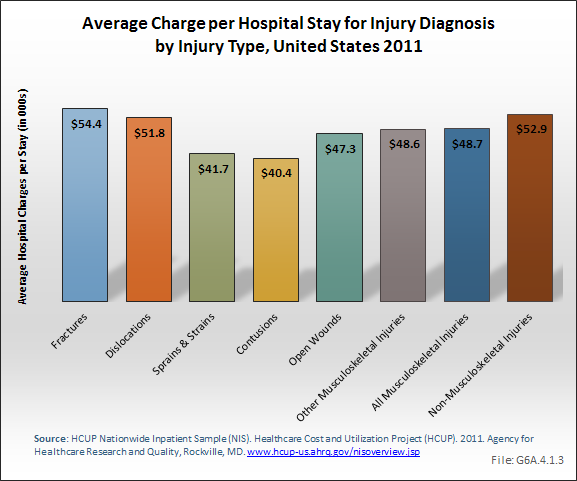
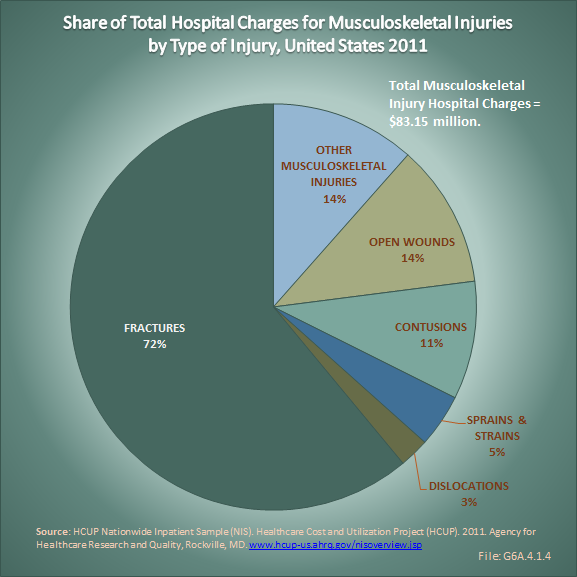
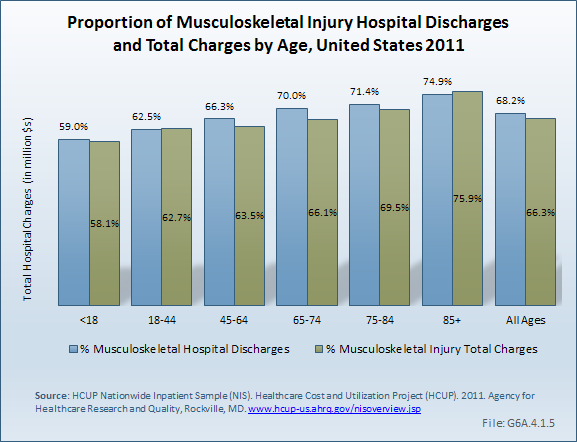
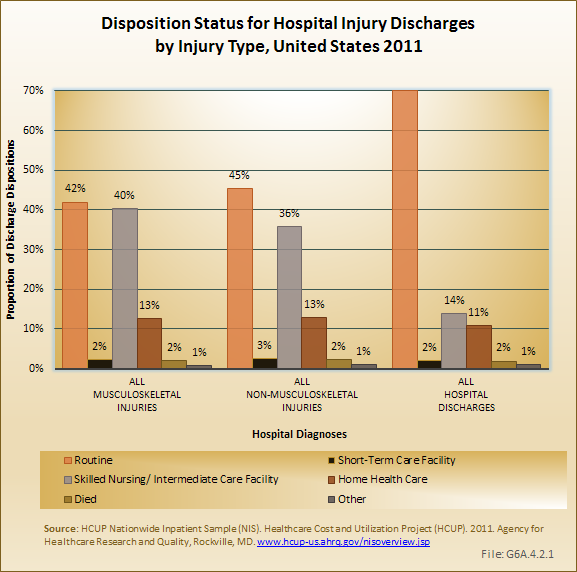
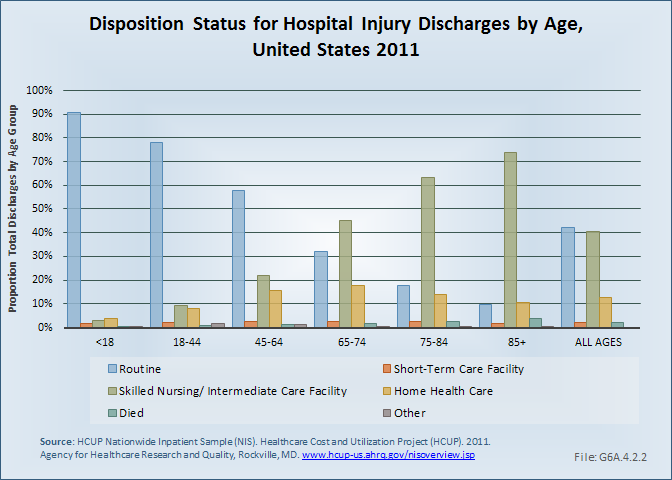
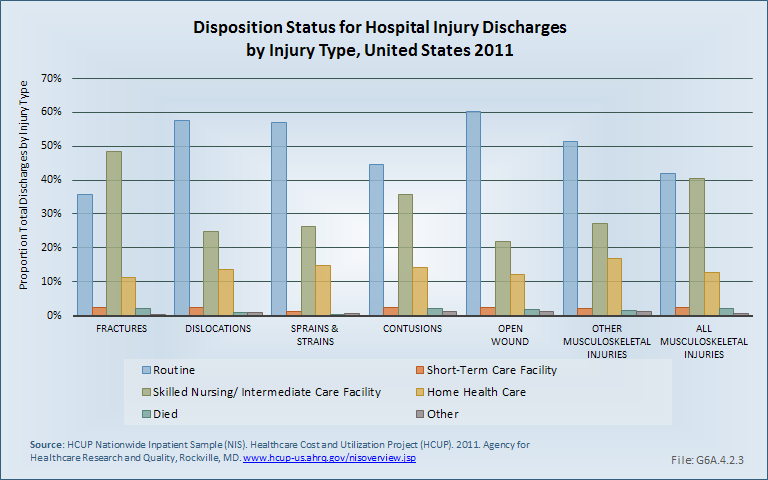
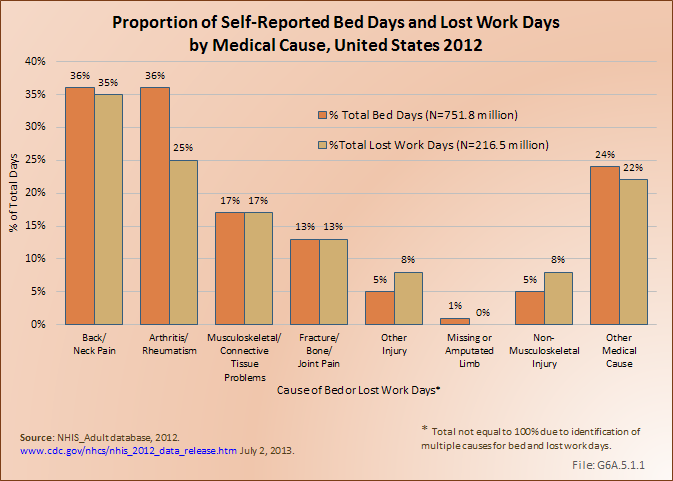
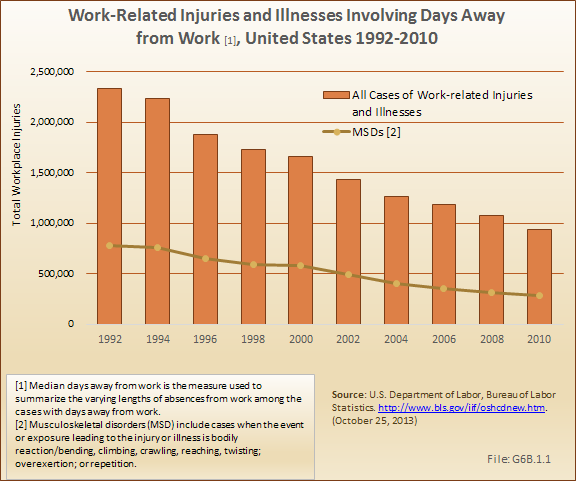
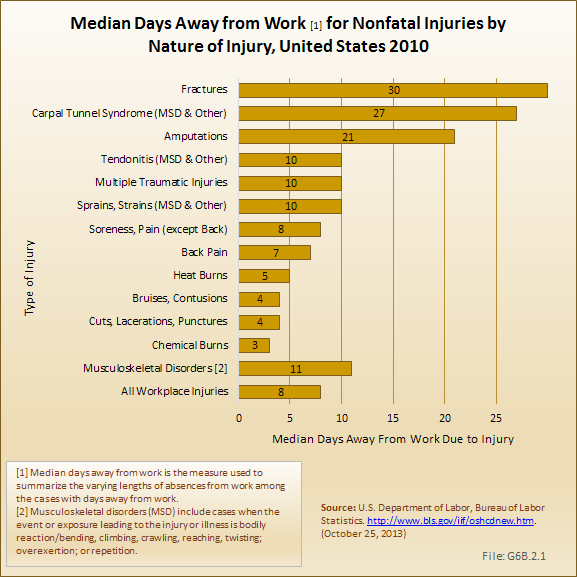
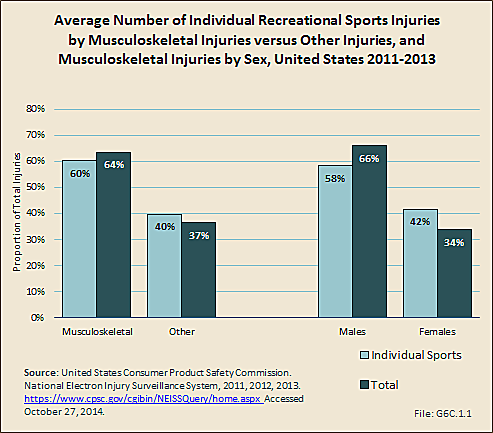
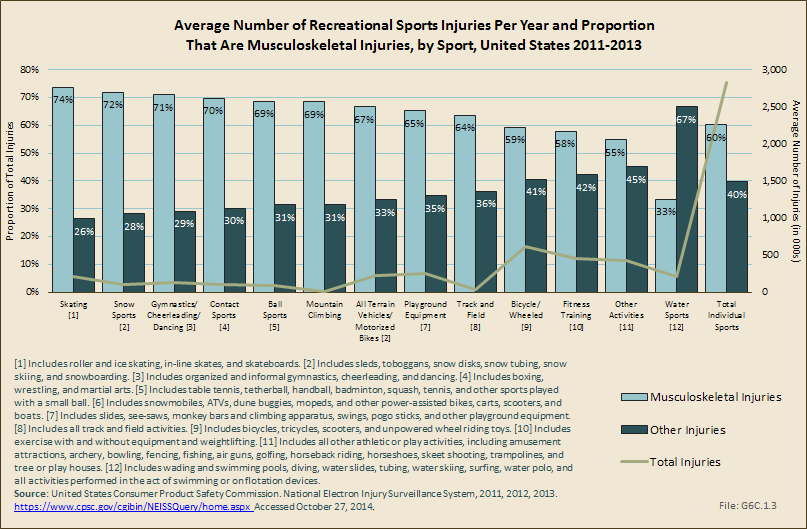
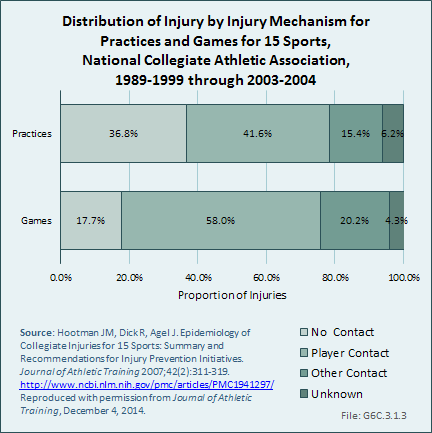
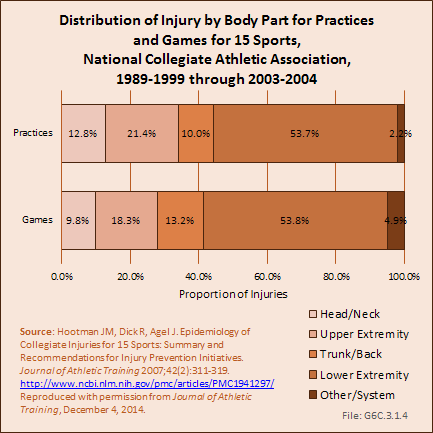
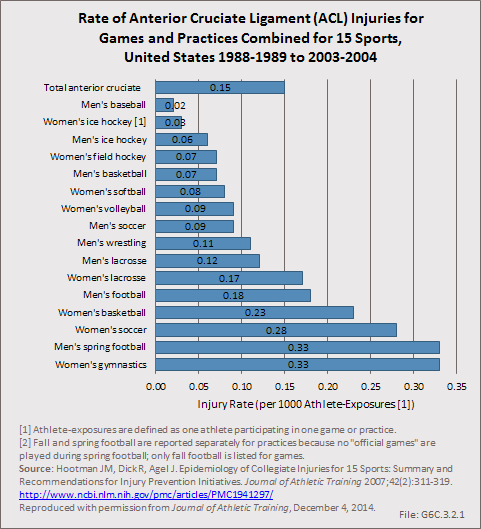
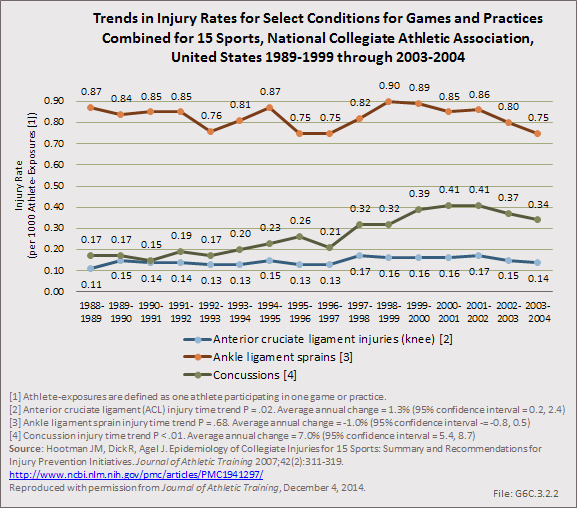
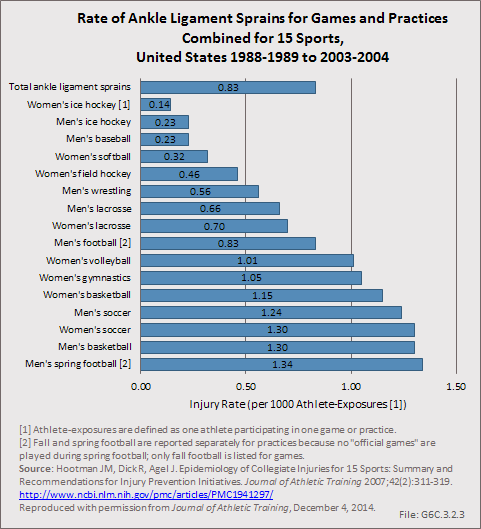
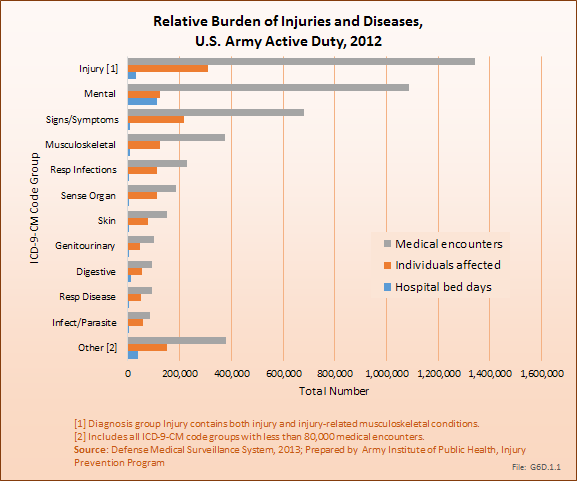
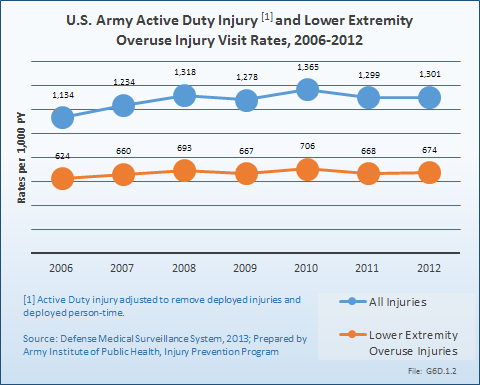

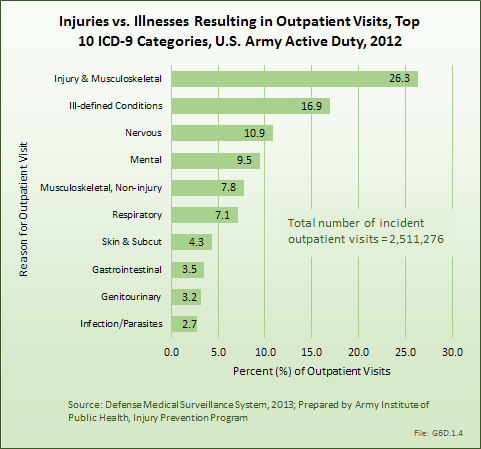
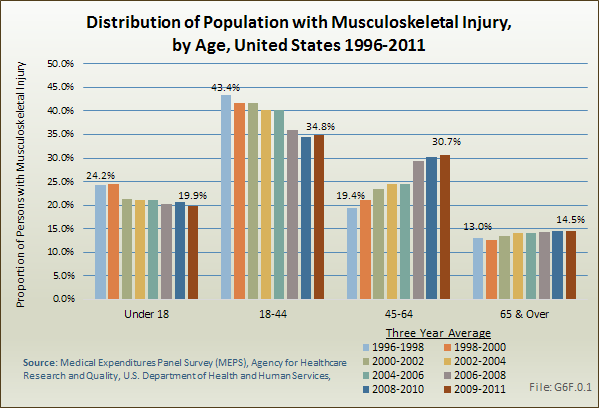
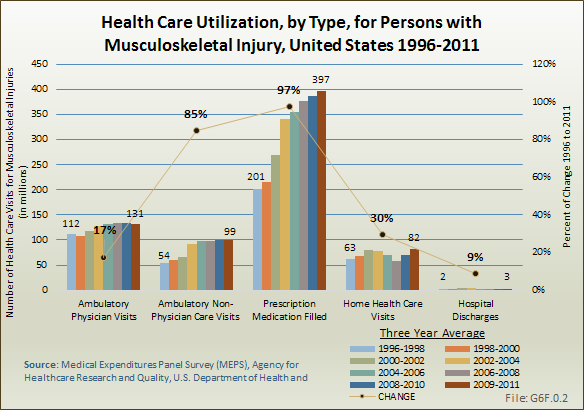
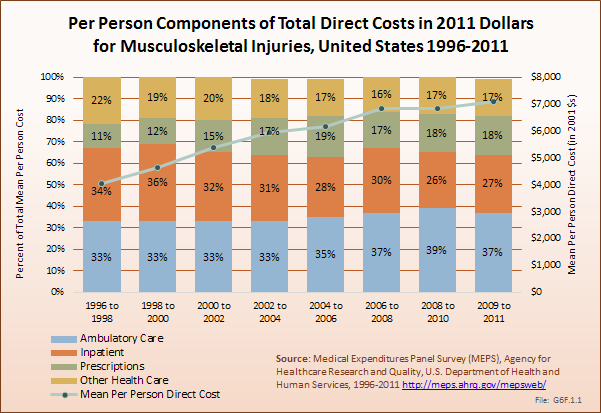
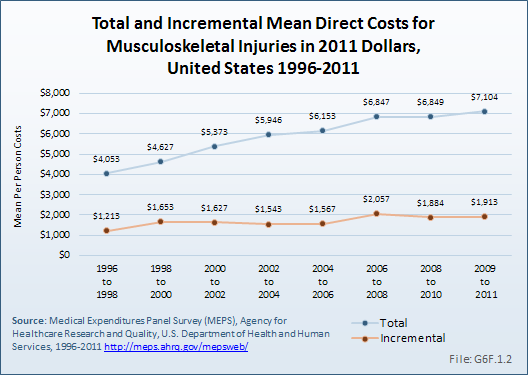
 Download as CSV
Download as CSV