Children & Adolescents
VII.B.1.0
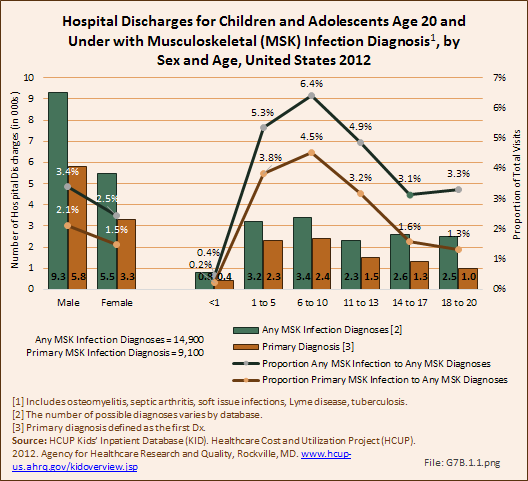
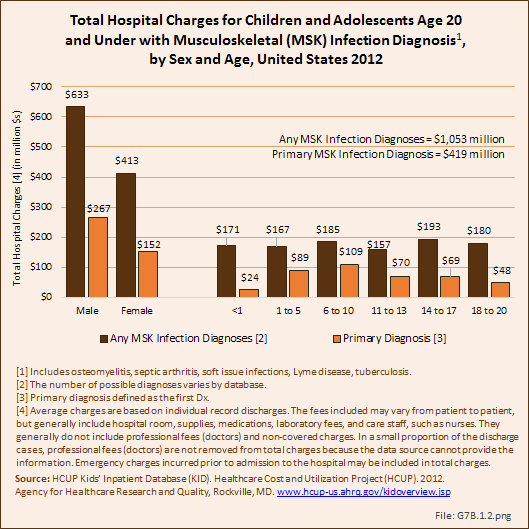
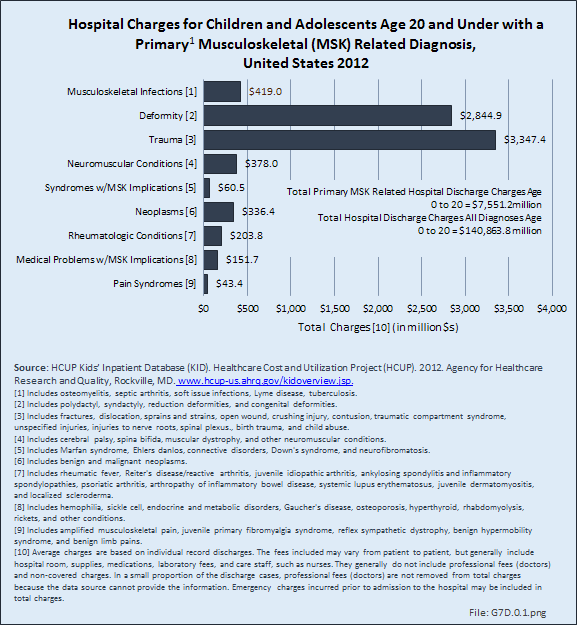
Musculoskeletal infections included in this section are osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, soft tissue infections (myositis), Lyme disease, and tuberculosis. Osteomyelitis and septic arthritis are the most common form of pediatric musculoskeletal infections and most commonly occur in the first decade of life in previously healthy children. Lyme disease is caused by a bite from a deer tick and is less common than osteomyelitis and septic arthritis. It is more prevalent in the Northeastern and Midwestern regions of the United States.1 Tuberculosis (TB) has become much less common in the United States over the last few decades, but has increased in incidence in developing countries secondary to immunodeficiency and multidrug resistance. TB infections involve the musculoskeletal system in 2% to 5% of cases.2 Community-acquired Staphylococcus aureus (CA-SA) is the most common infecting organism in pediatric musculoskeletal infections and is typically treated with a first-generation cephalosporin, such as cefazolin. Over the past decade methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) has become prevalent and requires treatment with second-line antibiotics such as clindamycin or vancomycin.3 As MRSA infections have become more prevalent, the disease course for patients with these infections has become much more severe, with greater systemic disease requiring multimodal and multidisciplinary treatments including medical, surgical, and critical care. Patients are often hospitalized for extended periods and most require continued care with long-term antibiotic treatment after discharge. Complications of musculoskeletal infections include growth deformity, fractures, and arthritis, and may result in long-term morbidity and dysfunction.
- 1. Willis AA, Widmann RF, Flynn JM, Green DW, Onel KB: Lyme arthritis presenting as acute septic arthritis in children. J Pediatr Orthop 2003 Jan-Feb;23(1):114-118.
- 2. Rasool MN: Osseous manifestations of tuberculosis in children. J Pediatr Orthop 2001 Nov-Dec;21(6):749-755.
- 3. Copley LA: Pediatric musculoskeletal infection: Trends and antibiotic recommendations. JAAOS 2009 Oct;17(10):618-626. PubMed PMID: 19794219. Epub 2009/10/02. eng.
Edition:
- 2014

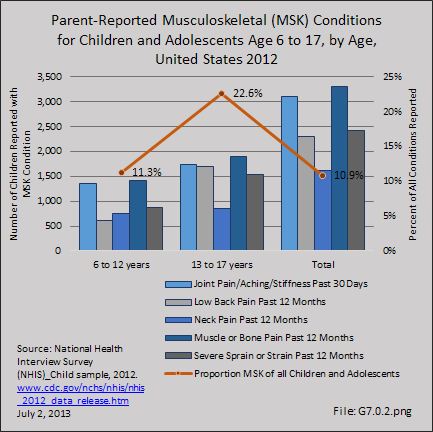

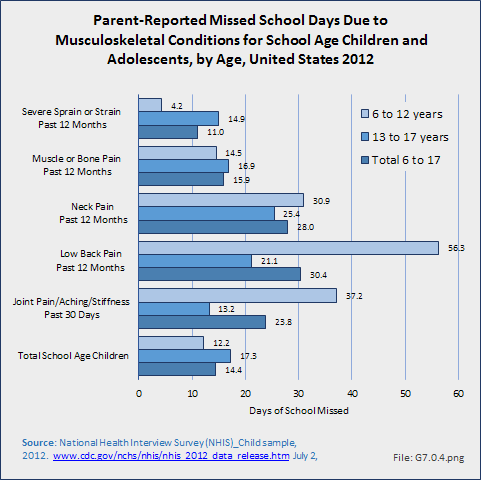
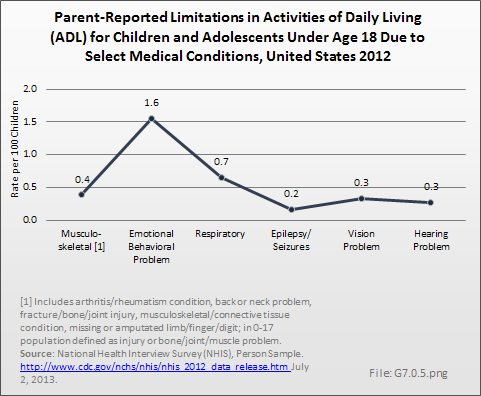

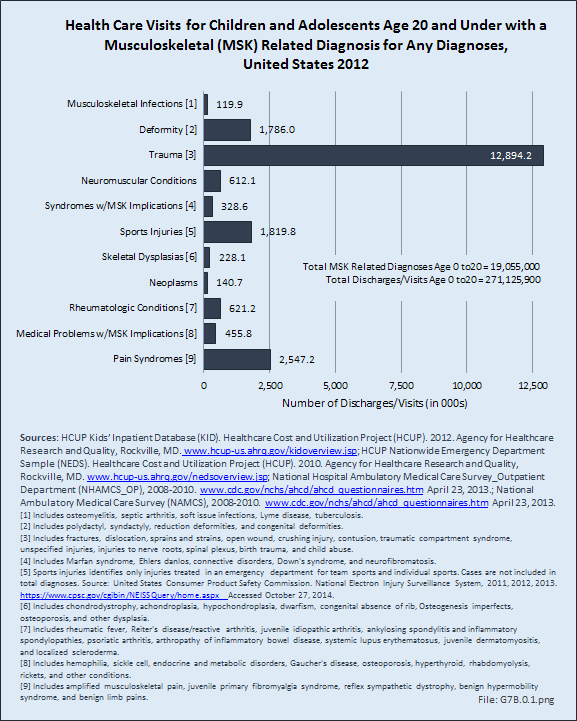


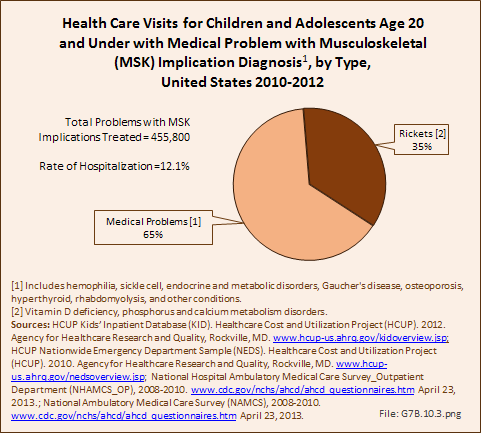
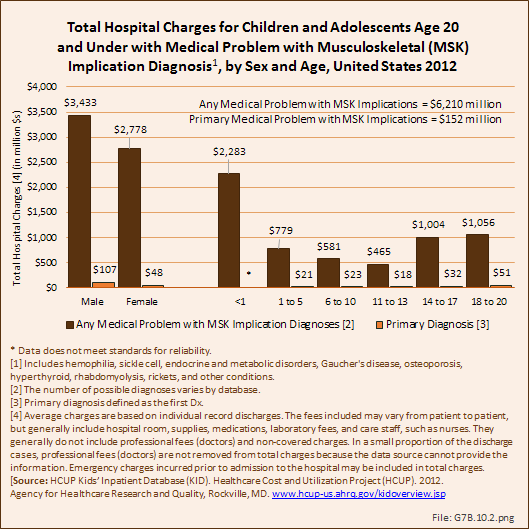

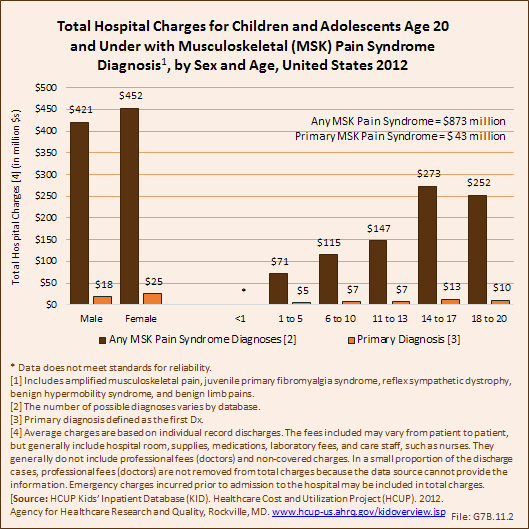
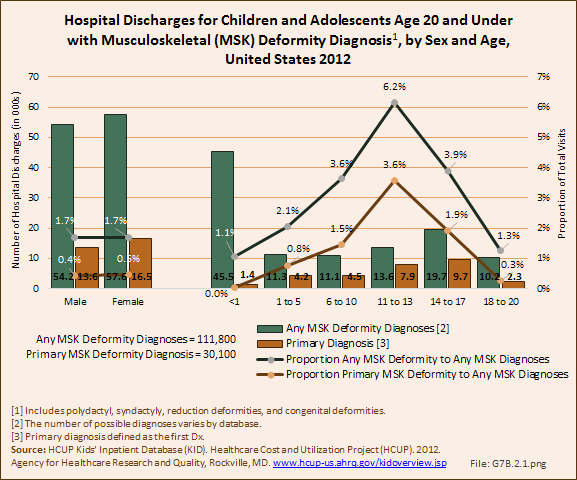
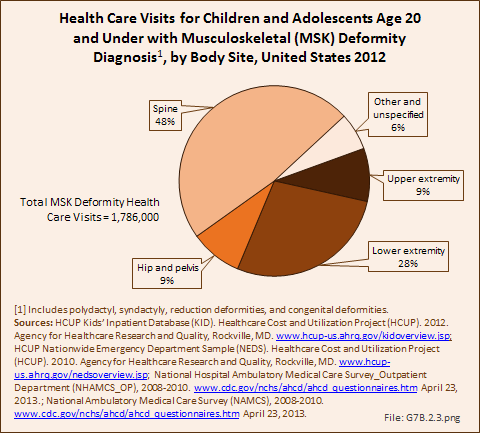
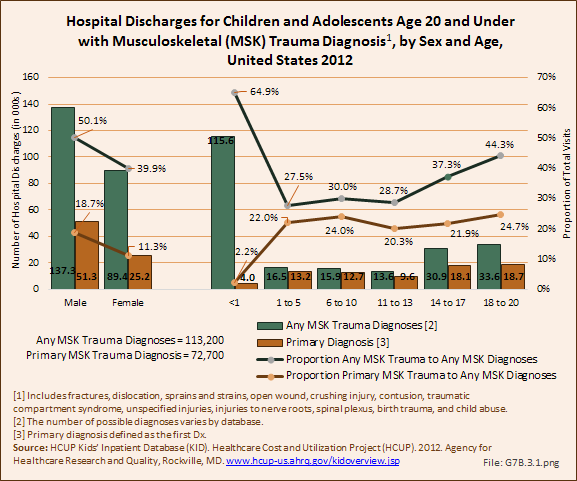
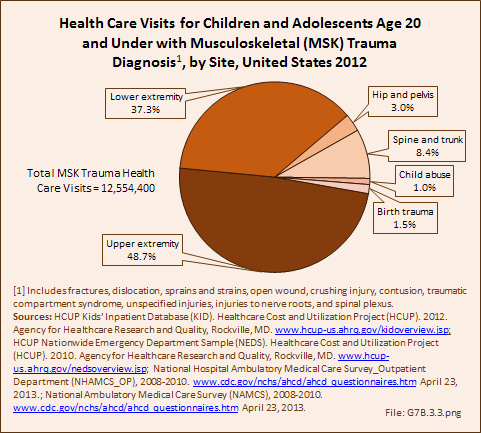


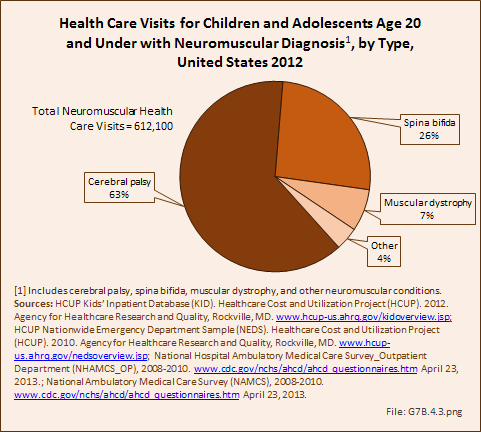
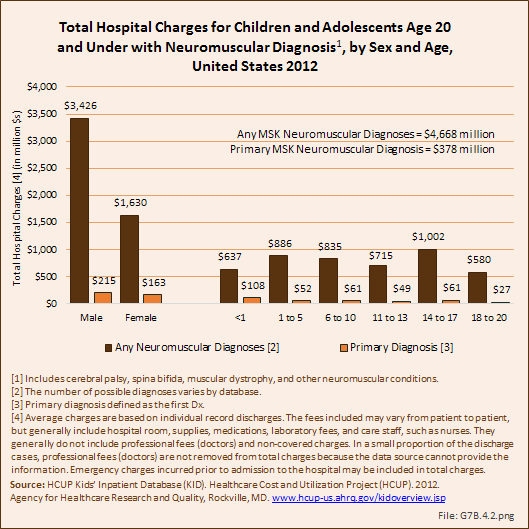
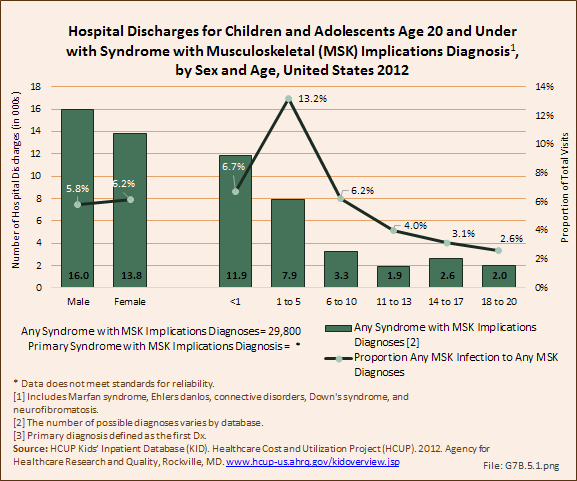
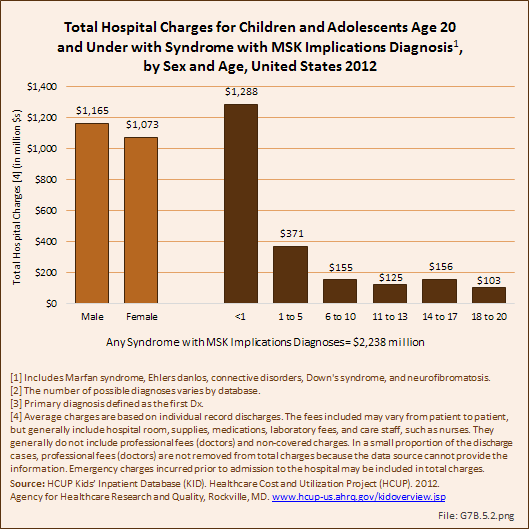
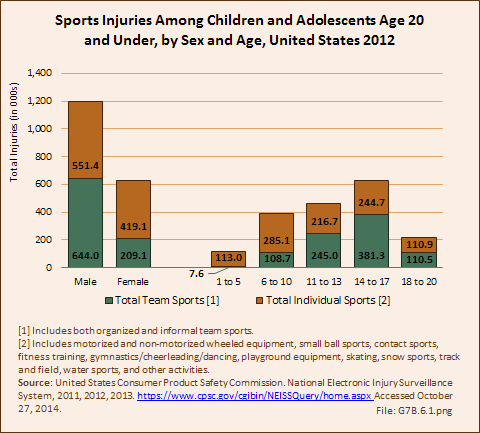



 Download as CSV
Download as CSV