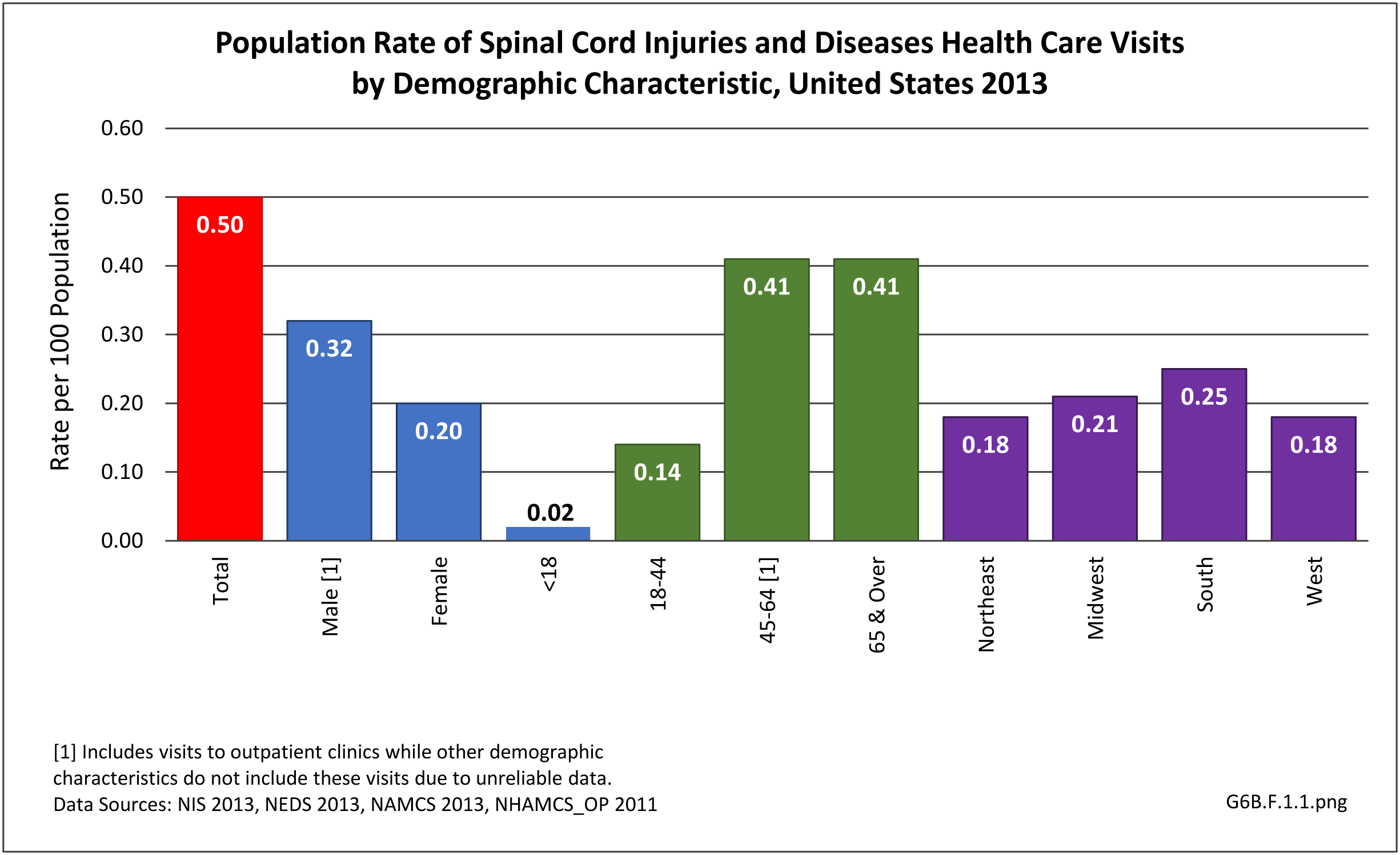
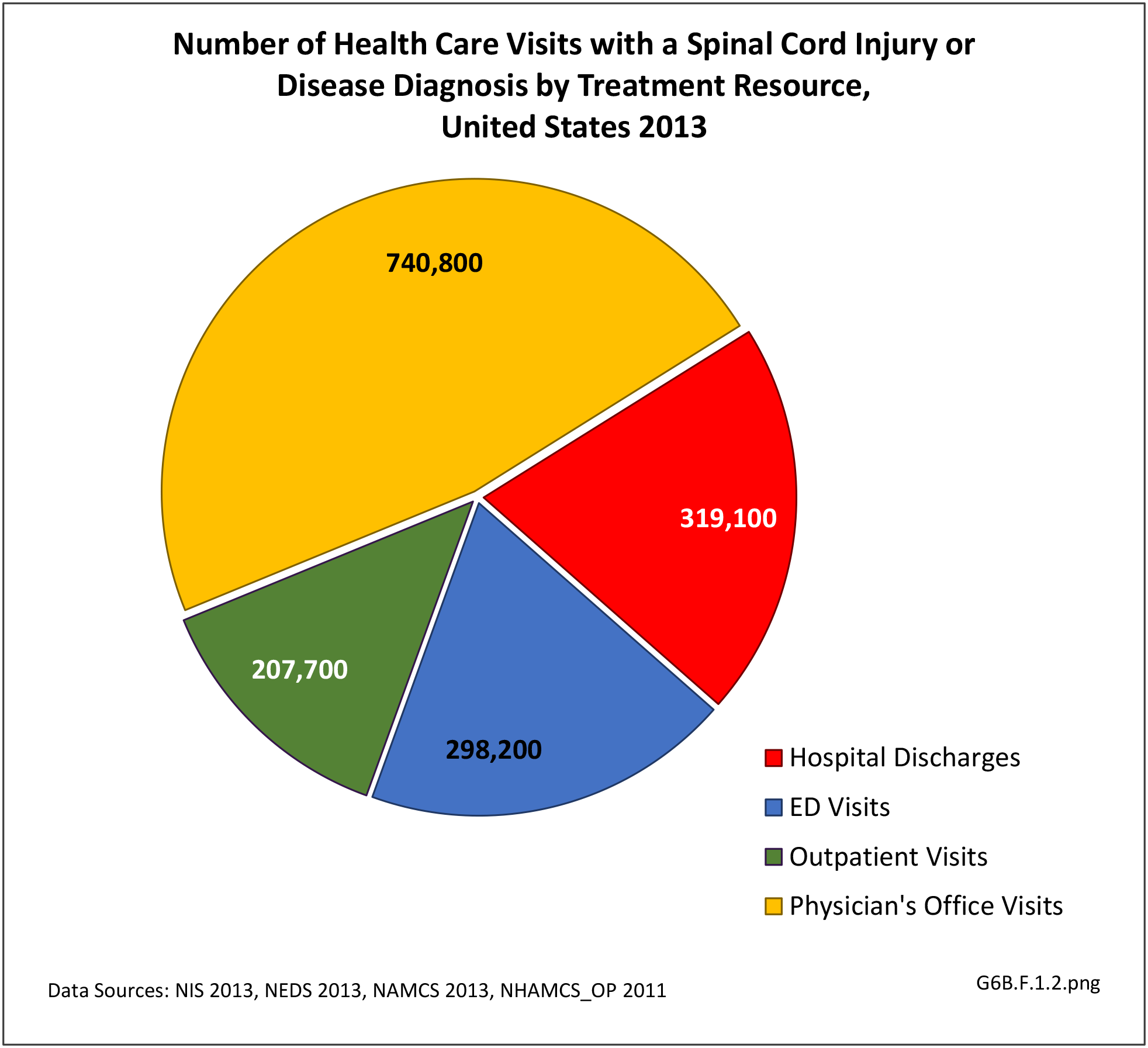
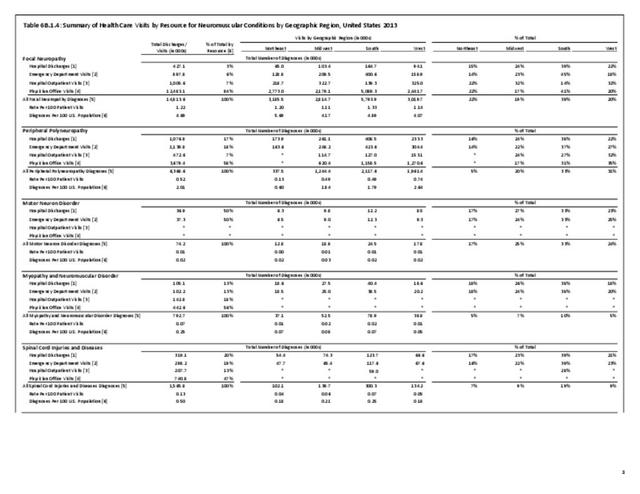
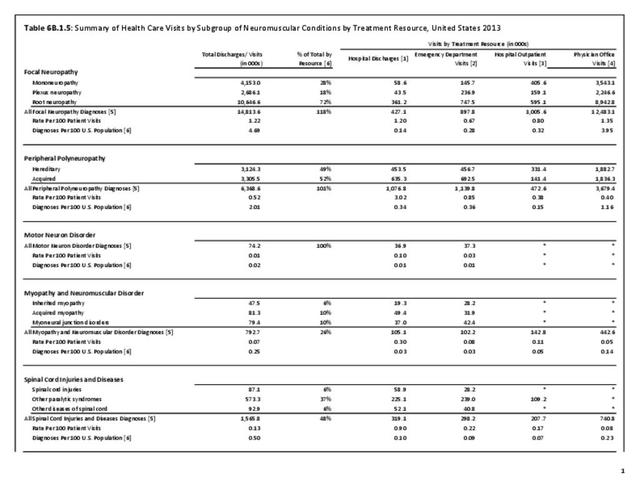
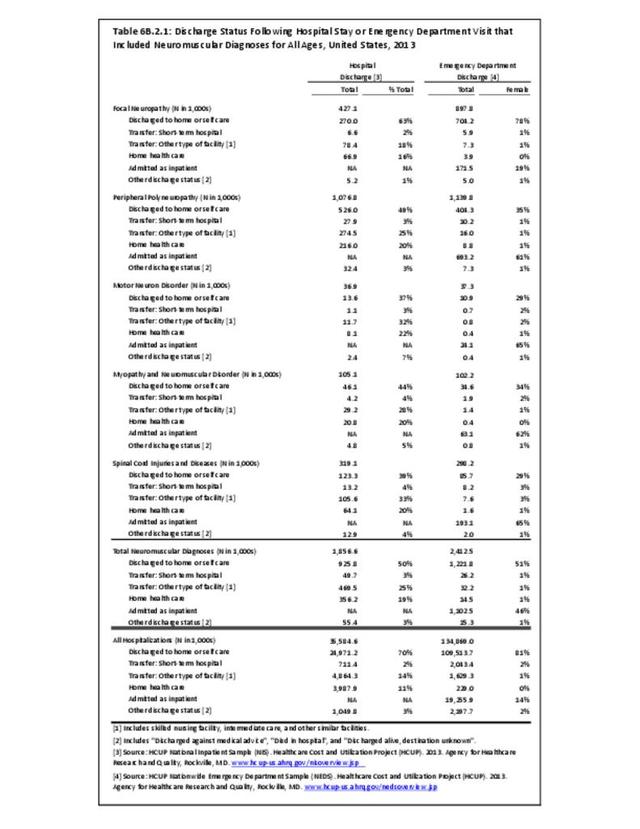
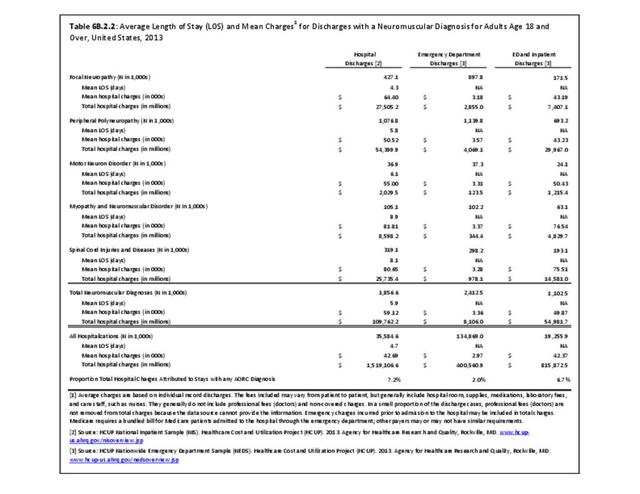
The overall burden of all neuromuscular conditions is difficult to assess due to the life-long care usually required following onset of the disease. However, comparison of the 1.9 million hospital discharges and 2.4 million emergency department visits for all health conditions provides some sense of the magnitude of burden.
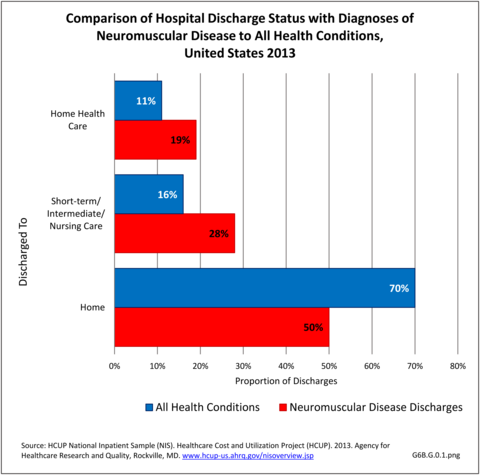
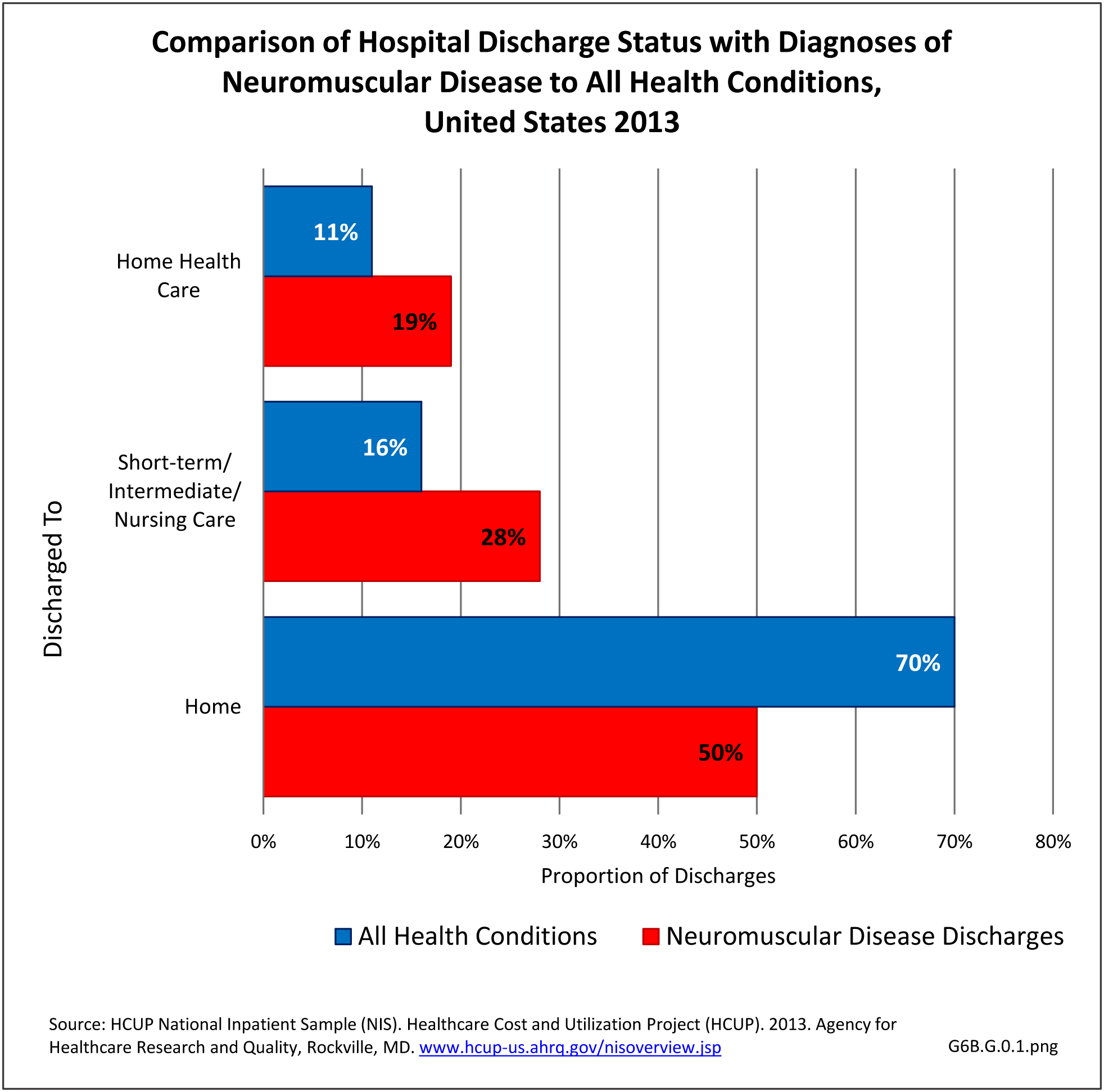
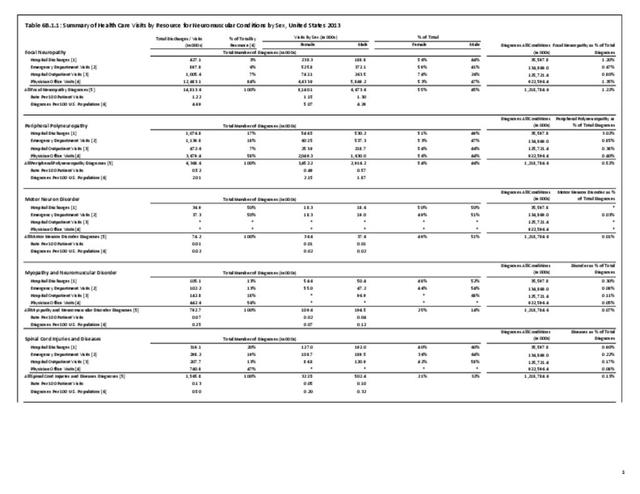
Neuromuscular conditions were 5% of all hospital discharges and 2% of all emergency department visits in 2013. Discharge from the hospital to another form of care (short/intermediate/nursing home facility or home health care) occurred in 47% of discharges with a neuromuscular diagnosis, compared to 27% of discharges for all health care reasons. Among ED visits, 46% were admitted to the hospital when there was a neuromuscular diagnosis, compared to 14% for all health care reasons. Thus, it can be seen than neuromuscular conditions have a much higher level of long-term care than health conditions overall. (Reference Table 6B.2.1 PDF CSV)
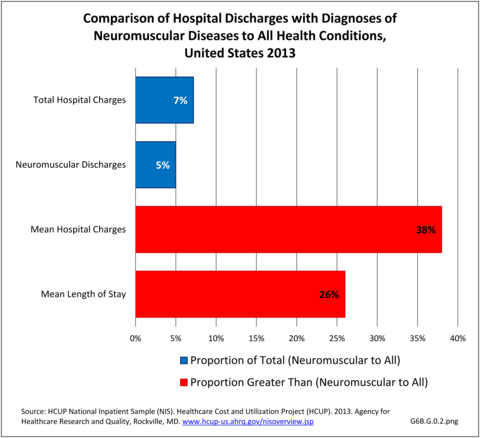
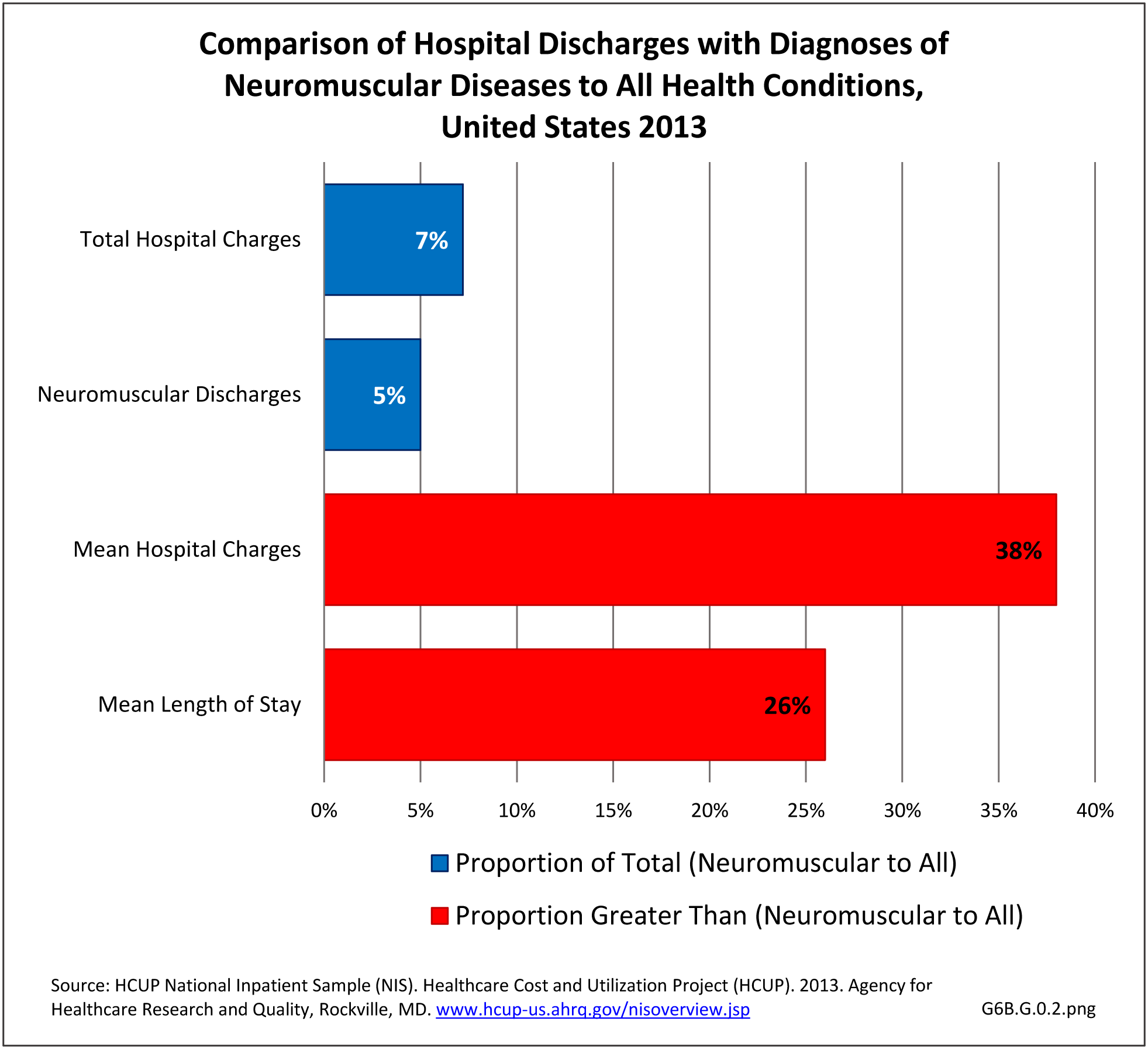
Mean hospital charges in 2013 for all discharges with a neuromuscular disease diagnosis were $59,100, 38% greater than mean charge for discharges with any health condition. Mean length of stay for persons with a neuromuscular disease were 26% longer than the mean stay for all hospitalizations (5.9 days versus 4.7 days. Total hospital charges for neuromuscular diseases in 2013 were $109.8 million, 7.2% of total hospital charges for all health conditions, even though discharges for a neuromuscular disease comprised only 5% of all hospitalizations. (Reference Table 6B.2.2 PDF CSV)
Edition:
- Fourth Edition