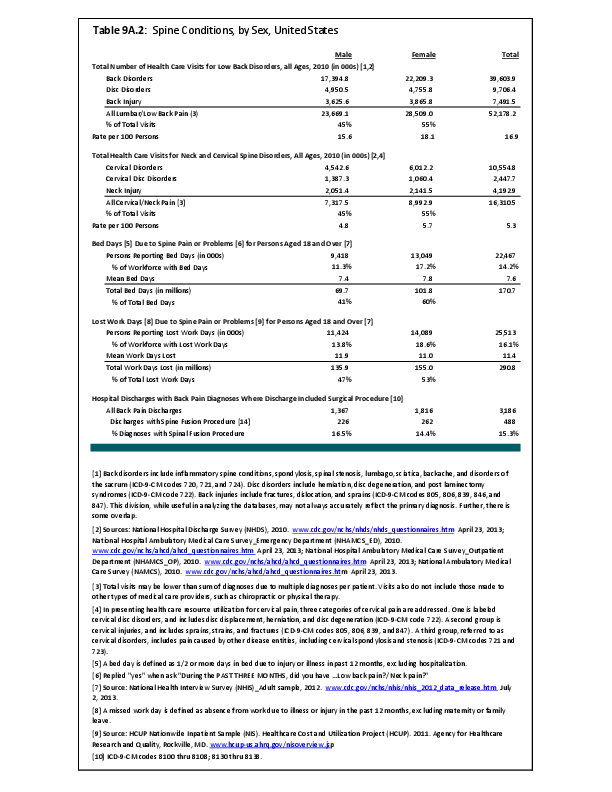
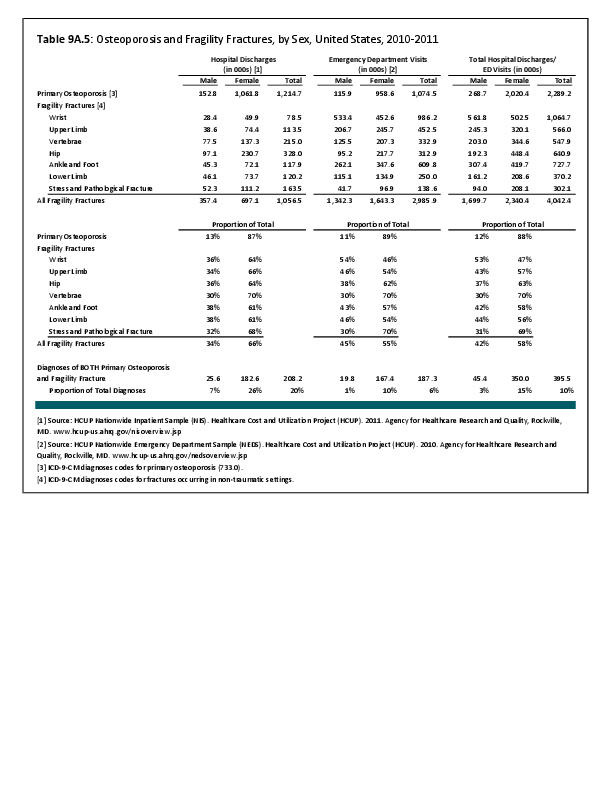
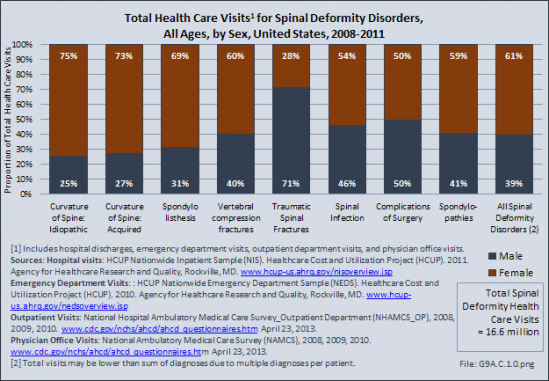
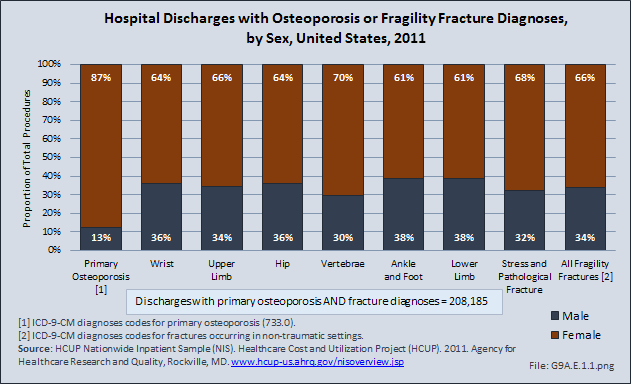
Although women represent 51% of the total population, they have a greater than expected rate of health care visits for the majority of spinal deformity disorders. This is particularly true for both idiopathic (75%) and acquired spinal curvature (73%), and for spondylolisthesis (69%), a spinal condition that causes one of the lower vertebra to slip forward onto the bone directly beneath it. Traumatic spinal fractures occur at a greater extent to men, while vertebral compression fractures, often due to osteoporosis, occur much more frequently in women. Spinal infections and complications from surgery related to spinal deformity occur about equally between men and women.
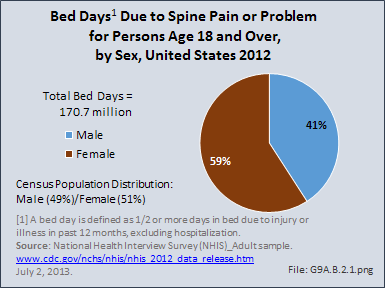
Spondylopathies, which refer to any disease of the vertebrae associated with compression of peripheral nerve roots and spinal cord, causing pain and stiffness, were diagnosed more frequently (59%) in health care visits by women than by men (41%).
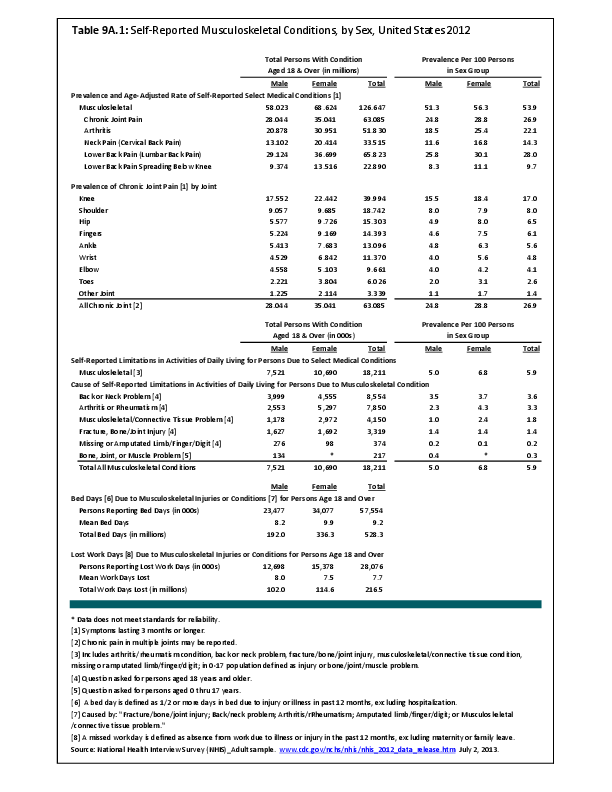
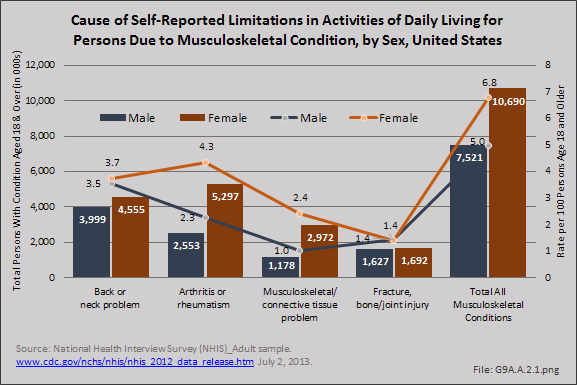
Overall, on an annual average, 16.6 million health care visits for spinal deformity conditions were made each year in the years 2008 to 2011. Of these visits, 61% of those treated were women. (Reference Table 9A.3 PDF CSV)
Edition:
- 2014









 Download as CSV
Download as CSV